Interorgan crosstalk in pancreatic islet function and pathology
- PMID: 35014695
- PMCID: PMC8930530
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14282
Interorgan crosstalk in pancreatic islet function and pathology
Abstract
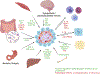
Pancreatic β cells secrete insulin in response to glucose, a process that is regulated at multiple levels, including a network of input signals from other organ systems. Impaired islet function contributes to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and targeting inter-organ communications, such as GLP-1 signalling, to enhance β-cell function has been proven to be a successful therapeutic strategy in the last decade. In this review, we will discuss recent advances in inter-organ communication from the metabolic, immune and neural system to pancreatic islets, their biological implication in normal pancreas endocrine function and their role in the (mal)adaptive responses of islet to nutrition-induced stress.
Keywords: GLP-1; inter-organ crosstalk; pancreatic β cells; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2022 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Diabetes Statistics Report. in https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-stat....
-
- Donath MY, Dalmas E, Sauter NS & Boni-Schnetzler M (2013) Inflammation in obesity and diabetes: islet dysfunction and therapeutic opportunity, Cell metabolism. 17, 860–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

