Utilization Rates of SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Their Facility-Level Variation Among Patients With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Insights From the Department of Veterans Affairs
- PMID: 35015080
- PMCID: PMC8914426
- DOI: 10.2337/dc21-1815
Utilization Rates of SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Their Facility-Level Variation Among Patients With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Insights From the Department of Veterans Affairs
Abstract
Objective: There is mounting evidence regarding the cardiovascular benefits of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) among patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). There is paucity of data assessing real-world practice patterns for these drug classes. We aimed to assess utilization rates of these drug classes and facility-level variation in their use.
Research design and methods: We used the nationwide Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system data set from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2020 and included patients with established ASCVD and T2DM. Among these patients, we assessed the use of SGLT2i and GLP-1 RA and the facility-level variation in their use. Facility-level variation was computed using median rate ratios (MRR), a measure of likelihood that two random facilities differ in use of SGLT2i and GLP-1 RA in patients with ASCVD and T2DM.
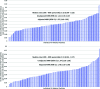
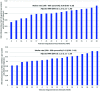
Results: Among 537,980 patients with ASCVD and T2DM across 130 VA facilities, 11.2% of patients received an SGLT2i while 8.0% of patients received a GLP-1 RA. Patients receiving these cardioprotective glucose-lowering drug classes were on average younger and had a higher proportion of non-Hispanic Whites. Overall, median (10th-90th percentile) facility-level rates were 14.92% (9.31-22.50) for SGLT2i and 10.88% (4.44-17.07) for GLP-1 RA. There was significant facility-level variation among SGLT2i use-MRRunadjusted: 1.41 (95% CI 1.35-1.47) and MRRadjusted: 1.55 (95% CI 1.46 -1.63). Similar facility-level variation was observed for use of GLP-1 RA-MRRunadjusted: 1.34 (95% CI 1.29-1.38) and MRRadjusted: 1.78 (95% CI 1.65-1.90).
Conclusions: Overall utilization rates of SGLT2i and GLP-1 RA among eligible patients are low, with significantly higher residual facility-level variation in the use of these drug classes. Our results suggest opportunities to optimize their use to prevent future adverse cardiovascular events among these patients.
© 2022 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Tsapas A, Avgerinos I, Karagiannis T, et al. Comparative effectiveness of glucose-lowering drugs for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2020;173:278–286 - PubMed
-
- Zhu J, Yu X, Zheng Y, et al. Association of glucose-lowering medications with cardiovascular outcomes: an umbrella review and evidence map. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2020;8:192–205 - PubMed
-
- Brown E, Heerspink HJL, Cuthbertson DJ, Wilding JPH. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: established and emerging indications. Lancet 2021;398:262–276 - PubMed
-
- Lee MMY, Petrie MC, McMurray JJV, Sattar N. How do SGLT2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) inhibitors and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists reduce cardiovascular outcomes? Completed and ongoing mechanistic trials. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2020;40:506–522 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical