Interaction of obesity polygenic score with lifestyle risk factors in an electronic health record biobank
- PMID: 35016652
- PMCID: PMC8753909
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-021-02198-9
Interaction of obesity polygenic score with lifestyle risk factors in an electronic health record biobank
Abstract
Background: Genetic and lifestyle factors have considerable effects on obesity and related diseases, yet their effects in a clinical cohort are unknown. This study in a patient biobank examined associations of a BMI polygenic risk score (PRS), and its interactions with lifestyle risk factors, with clinically measured BMI and clinical phenotypes.
Methods: The Mass General Brigham (MGB) Biobank is a hospital-based cohort with electronic health record, genetic, and lifestyle data. A PRS for obesity was generated using 97 genetic variants for BMI. An obesity lifestyle risk index using survey responses to obesogenic lifestyle risk factors (alcohol, education, exercise, sleep, smoking, and shift work) was used to dichotomize the cohort into high and low obesogenic index based on the population median. Height and weight were measured at a clinical visit. Multivariable linear cross-sectional associations of the PRS with BMI and interactions with the obesity lifestyle risk index were conducted. In phenome-wide association analyses (PheWAS), similar logistic models were conducted for 675 disease outcomes derived from billing codes.
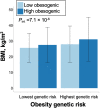
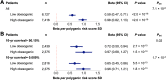
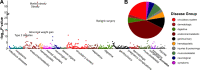
Results: Thirty-three thousand five hundred eleven patients were analyzed (53.1% female; age 60.0 years; BMI 28.3 kg/m2), of which 17,040 completed the lifestyle survey (57.5% female; age: 60.2; BMI: 28.1 (6.2) kg/m2). Each standard deviation increment in the PRS was associated with 0.83 kg/m2 unit increase in BMI (95% confidence interval (CI) =0.76, 0.90). There was an interaction between the obesity PRS and obesity lifestyle risk index on BMI. The difference in BMI between those with a high and low obesogenic index was 3.18 kg/m2 in patients in the highest decile of PRS, whereas that difference was only 1.55 kg/m2 in patients in the lowest decile of PRS. In PheWAS, the obesity PRS was associated with 40 diseases spanning endocrine/metabolic, circulatory, and 8 other disease groups. No interactions were evident between the PRS and the index on disease outcomes.
Conclusions: In this hospital-based clinical biobank, obesity risk conferred by common genetic variants was associated with elevated BMI and this risk was attenuated by a healthier patient lifestyle. Continued consideration of the role of lifestyle in the context of genetic predisposition in healthcare settings is necessary to quantify the extent to which modifiable lifestyle risk factors may moderate genetic predisposition and inform clinical action to achieve personalized medicine.
Keywords: BMI; Electronic health records; Gene-lifestyle interaction; Genetic risk; Lifestyle; Obesity; Obesogenic behaviors; Phenome-wide association study.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
HSD, NM, BEC, TH, EWK, and RS have no competing interests. SR reports grant and consulting support from Jazz Pharma, and consulting fees from Eisai Pharma, Apnimed Inc and Eli Lilly Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon MN, Zeggini E, Freathy RM, Lindgren CM, Perry JRB, Elliott KS, Lango H, Rayner NW, Shields B, Harries LW, Barrett JC, Ellard S, Groves CJ, Knight B, Patch AM, Ness AR, Ebrahim S, Lawlor DA, Ring SM, Ben-Shlomo Y, Jarvelin MR, Sovio U, Bennett AJ, Melzer D, Ferrucci L, Loos RJF, Barroso IÌ, Wareham NJ, Karpe F, Owen KR, Cardon LR, Walker M, Hitman GA, Palmer CNA, Doney ASF, Morris AD, Smith GD, Hattersley AT, McCarthy MI. A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science. 2007;316(5826):889–894. doi: 10.1126/science.1141634. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yengo L, Sidorenko J, Kemper KE, Zheng Z, Wood AR, Weedon MN, Frayling TM, Hirschhorn J, Yang J, Visscher PM, the GIANT Consortium Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for height and body mass index in ~700 000 individuals of European ancestry. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(20):3641–3649. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy271. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153805/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35HL135818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2OD026553/NIH Office of the Director
- K01HL143034/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL143034/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL135405/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146751/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK105072/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK107859/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL113338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99HL153795/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL154284/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG008685/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

