HDAC8 suppresses the epithelial phenotype and promotes EMT in chemotherapy-treated basal-like breast cancer
- PMID: 35016723
- PMCID: PMC8753869
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-022-01228-4
HDAC8 suppresses the epithelial phenotype and promotes EMT in chemotherapy-treated basal-like breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) is one of the most aggressive malignant diseases in women with an increased metastatic behavior and poor prognosis compared to other molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Resistance to chemotherapy is the main cause of treatment failure in BLBC. Therefore, novel therapeutic strategies counteracting the gain of aggressiveness underlying therapy resistance are urgently needed. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) has been established as one central process stimulating cancer cell migratory capacity but also acquisition of chemotherapy-resistant properties. In this study, we aimed to uncover epigenetic factors involved in the EMT-transcriptional program occurring in BLBC cells surviving conventional chemotherapy.
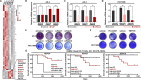
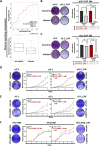
Results: Using whole transcriptome data from a murine mammary carcinoma cell line (pG-2), we identified upregulation of Hdac4, 7 and 8 in tumor cells surviving conventional chemotherapy. Subsequent analyses of human BLBC patient datasets and cell lines established HDAC8 as the most promising factor sustaining tumor cell viability. ChIP-sequencing data analysis identified a pronounced loss of H3K27ac at regulatory regions of master transcription factors (TFs) of epithelial phenotype like Gata3, Elf5, Rora and Grhl2 upon chemotherapy. Interestingly, impairment of HDAC8 activity reverted epithelial-TFs levels. Furthermore, loss of HDAC8 activity sensitized tumor cells to chemotherapeutic treatments, even at low doses.
Conclusion: The current study reveals a previously unknown transcriptional repressive function of HDAC8 exerted on a panel of transcription factors involved in the maintenance of epithelial cell phenotype, thereby supporting BLBC cell survival to conventional chemotherapy. Our data establish HDAC8 as an attractive therapeutically targetable epigenetic factor to increase the efficiency of chemotherapeutics.
Keywords: BLBC; Chemotherapy; EMT; Epigenetics; Epithelial transcription factors; H3K27ac; HDAC8; MET; TNBC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

