Non-viral vectors for RNA delivery
- PMID: 35016918
- PMCID: PMC8743282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.01.008
Non-viral vectors for RNA delivery
Abstract
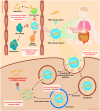
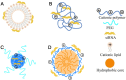
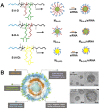
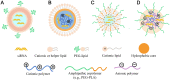
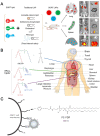
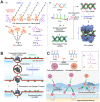
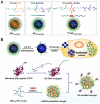
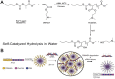
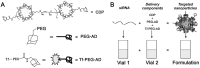
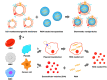
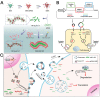
RNA-based therapy is a promising and potential strategy for disease treatment by introducing exogenous nucleic acids such as messenger RNA (mRNA), small interfering RNA (siRNA), microRNA (miRNA) or antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) to modulate gene expression in specific cells. It is exciting that mRNA encoding the spike protein of COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) delivered by lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) exhibits the efficient protection of lungs infection against the virus. In this review, we introduce the biological barriers to RNA delivery in vivo and discuss recent advances in non-viral delivery systems, such as lipid-based nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc)-siRNA conjugate, and biomimetic nanovectors, which can protect RNAs against degradation by ribonucleases, accumulate in specific tissue, facilitate cell internalization, and allow for the controlled release of the encapsulated therapeutics.
Keywords: Biological barrier; Control release; Gene therapy; Non-viral vector; RNA drugs.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors stated that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Jan 4;55(1):2-12. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00544. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 34850635 Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticle formulations for optimal RNA-based topical delivery to murine airways.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022 Sep 1;176:106234. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106234. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35688311
-
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for in vivo RNA delivery and their breakthrough technology for future applications.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023 Sep;200:114990. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.114990. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023. PMID: 37423563 Review.
-
Optimization of phospholipid chemistry for improved lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery of messenger RNA (mRNA).Biomater Sci. 2022 Jan 18;10(2):549-559. doi: 10.1039/d1bm01454d. Biomater Sci. 2022. PMID: 34904974 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic intranasal administration of lipid nanoparticle formulated siRNAs reduce SARS-CoV-2 and RSV lung infection.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2023 Jun;56(3):516-525. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2023.02.010. Epub 2023 Mar 8. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2023. PMID: 36934064 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unraveling Therapeutic Opportunities and the Diagnostic Potential of microRNAs for Human Lung Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 31;15(8):2061. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082061. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress on RNA-based therapeutics for genetic diseases.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Aug 25;52(4):406-416. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2023-0190. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37643975 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Advanced siRNA delivery in combating hepatitis B virus: mechanistic insights and recent updates.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Nov 30;22(1):745. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-03004-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39616384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Synthesis of miR-200c-3p Lipid Nanoparticles: Targeting ZEB2 to Alleviate Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jan 14;20:505-521. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S491711. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39830158 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the mechanism of exosome-mediated virus infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jun 26;14:1418168. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1418168. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38988816 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anguela X.M., High K.A. Entering the modern era of gene therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019;70:273–288. - PubMed
-
- Jeon Y.H., Jung Y.T. Production of a replicating retroviral vector expressing Reovirus fast protein for cancer gene therapy. J. Virol. Methods. 2022;299:114332. - PubMed
-
- Miname M.H., Rocha V.Z., Santos R.D. The role of RNA-targeted therapeutics to reduce ASCVD risk: what have we learned recently? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021;23(8):40. - PubMed
-
- Kulkarni J.A., Witzigmann D., Thomson S.B., Chen S., Leavitt B.R., Cullis P.R., van der Meel R. Author correction: the current landscape of nucleic acid therapeutics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021;16(7):841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

