Postganglionic Sudomotor Assessment in Early Stage of Multiple System Atrophy and Parkinson Disease: A Morpho-functional Study
- PMID: 35017309
- PMCID: PMC8967330
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000013300
Postganglionic Sudomotor Assessment in Early Stage of Multiple System Atrophy and Parkinson Disease: A Morpho-functional Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Sudomotor impairment has been recognized as a key feature in differentiating Parkinson disease (PD) and multiple system atrophy-parkinsonian type (MSA-P), with the latter characterized by diffuse anhidrosis in prospective study, including patients in late stage of disease. We aimed to evaluate morphologic and functional postganglionic sudomotor involvement in patients with newly diagnosed MSA-P and PD to identify possible biomarkers that might be of help in differentiating the 2 conditions in the early stage.
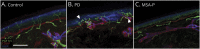
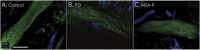
Methods: One hundred patients with parkinsonism within 2 years from onset of motor symptoms were included in the study. At the time of recruitment, questionnaires to assess nonmotor, autonomic, and small fiber symptoms were administered, and patients underwent postganglionic sudomotor function assessment by the dynamic sweat test and punch skin biopsy from the distal leg. Skin samples were processed for indirect immunofluorescence with a panel of antibodies, including noradrenergic and cholinergic markers. The density of intraepidermal, sudomotor, and pilomotor nerve fibers was measured on confocal images with dedicated software. A follow-up visit 12 months after recruitment was performed to confirm the diagnosis.
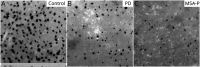
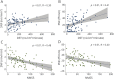
Results: We recruited 57 patients with PD (M/F 36/21, age 63.5 ± 9.4 years) and 43 patients with MSA-P (M/F 27/16, age 62.3 ± 9.0 years). Clinical scales and questionnaires showed a more severe clinical picture in patients with MSA-P compared to those with PD. Sweating output and intraepidermal, pilomotor, and sudomotor nerve densities, compared to controls, were lower in both groups but with a greater impairment in patients with MSA-P. Pilomotor and sudomotor nerve density correlated with sweating function and with nonmotor clinical symptoms. A composite sudomotor parameter defined as the arithmetic product of sweat production multiplied by the density of sudomotor fibers efficiently separated the 2 populations; the receiver operating characteristics curve showed an area under the curve of 0.83.
Discussion: Dynamic sweat test and the quantification of cutaneous autonomic nerves proved to be a sensitive morpho-functional approach to assess the postganglionic component of the sudomotor pathway, revealing a more severe involvement in MSA-P than in PD early in the disease course. This approach can be applied to differentiate the 2 conditions early.
Classification of evidence: This study provides Class II evidence that postganglionic sudomotor morpho-functional assessment accurately distinguish patients with PD from patients with MSA-P.
© 2022 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anhidrosis in multiple system atrophy involves pre- and postganglionic sudomotor dysfunction.Mov Disord. 2017 Mar;32(3):397-404. doi: 10.1002/mds.26864. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Mov Disord. 2017. PMID: 27859565 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated α-Synuclein Deposits in Cutaneous Nerves of Early Parkinsonism.J Parkinsons Dis. 2022;12(8):2453-2468. doi: 10.3233/JPD-223421. J Parkinsons Dis. 2022. PMID: 36373295
-
Cutaneous α-Synuclein Signatures in Patients With Multiple System Atrophy and Parkinson Disease.Neurology. 2023 Apr 11;100(15):e1529-e1539. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000206772. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Neurology. 2023. PMID: 36657992 Free PMC article.
-
Sudomotor Dysfunction.Semin Neurol. 2020 Oct;40(5):560-568. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1713847. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Semin Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32906168 Review.
-
Nonmotor Features in Atypical Parkinsonism.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017;134:1285-1301. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28805573 Review.
Cited by
-
Cutaneous nerve fiber pathology and function in Parkinson's disease and atypical parkinsonism - a cohort study.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025 Jun 15;11(1):170. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-01030-y. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 40517154 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of small fiber neuropathy in neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease: A clinicopathological study.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Feb;21(2):e14596. doi: 10.1002/alz.14596. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 39988644 Free PMC article.
-
Skin α-synuclein assays in diagnosing Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neurol. 2025 Apr 9;272(5):326. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-12978-5. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40205187
-
Multiple system atrophy.Pract Neurol. 2023 Jun;23(3):208-221. doi: 10.1136/pn-2020-002797. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Pract Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36927875 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- von Campenhausen S, Bornschein B, Wick R, et al. . Prevalence and incidence of Parkinson's disease in Europe. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2005;15(4):473-490. - PubMed
-
- Stankovic I, Petrovic I, Pekmezovic T, et al. . Longitudinal assessment of autonomic dysfunction in early Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019;66:74-79. - PubMed
-
- Osaki Y, Morita Y, Fukumoto M, Akagi N, Yoshida S, Doi Y. Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies of three-dimensional stereotactic surface projection SPECT analysis in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2009;24(10):1475-1480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
