Essential role of MALAT1 in reducing traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 35017438
- PMCID: PMC8820691
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.332156
Essential role of MALAT1 in reducing traumatic brain injury
Abstract
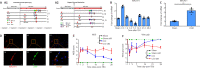
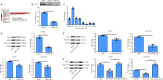
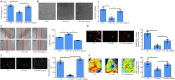
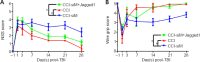
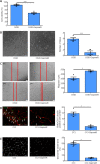
As a highly evolutionary conserved long non-coding RNA, metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) was first demonstrated to be related to lung tumor metastasis by promoting angiogenesis. To investigate the role of MALAT1 in traumatic brain injury, we established mouse models of controlled cortical impact and cell models of oxygen-glucose deprivation to mimic traumatic brain injury in vitro and in vivo. The results revealed that MALAT1 silencing in vitro inhibited endothelial cell viability and tube formation but increased migration. In MALAT1-deficient mice, endothelial cell proliferation in the injured cortex, functional vessel density and cerebral blood flow were reduced. Bioinformatic analyses and RNA pull-down assays validated enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) as a downstream factor of MALAT1 in endothelial cells. Jagged-1, the Notch homolog 1 (NOTCH1) agonist, reversed the MALAT1 deficiency-mediated impairment of angiogenesis. Taken together, our results suggest that MALAT1 controls the key processes of angiogenesis following traumatic brain injury in an EZH2/NOTCH1-dependent manner.
Keywords: EZH2; Jagged-1; LncRNA; MALAT1; NOTCH1; angiogenesis; controlled cortical impact; oxygen-glucose deprivation; traumatic brain injury; vascular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

References
-
- Asangani IA, Ateeq B, Cao Q, Dodson L, Pandhi M, Kunju LP, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Siddiqui J, Palanisamy N, Wu YM, Cao X, Kim JH, Zhao M, Qin ZS, Iyer MK, Maher CA, Kumar-Sinha C, Varambally S, Chinnaiyan AM. Characterization of the EZH2-MMSET histone methyltransferase regulatory axis in cancer. Mol Cell. 2013;49:80–93. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beermann J, Piccoli MT, Viereck J, Thum T. Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: background, mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol Rev. 2016;96:1297–1325. - PubMed
-
- Brütsch R, Liebler SS, Wüstehube J, Bartol A, Herberich SE, Adam MG, Telzerow A, Augustin HG, Fischer A. Integrin cytoplasmic domain-associated protein-1 attenuates sprouting angiogenesis. Circ Res. 2010;107:592–601. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

