Robust differentiation of human enteroendocrine cells from intestinal stem cells
- PMID: 35017529
- PMCID: PMC8752608
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27901-5
Robust differentiation of human enteroendocrine cells from intestinal stem cells
Abstract
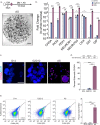
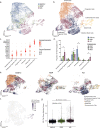
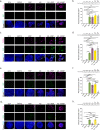
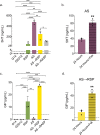
Enteroendocrine (EE) cells are the most abundant hormone-producing cells in humans and are critical regulators of energy homeostasis and gastrointestinal function. Challenges in converting human intestinal stem cells (ISCs) into functional EE cells, ex vivo, have limited progress in elucidating their role in disease pathogenesis and in harnessing their therapeutic potential. To address this, we employed small molecule targeting of the endocannabinoid receptor signaling pathway, JNK, and FOXO1, known to mediate endodermal development and/or hormone production, together with directed differentiation of human ISCs from the duodenum and rectum. We observed marked induction of EE cell differentiation and gut-derived expression and secretion of SST, 5HT, GIP, CCK, GLP-1 and PYY upon treatment with various combinations of three small molecules: rimonabant, SP600125 and AS1842856. Robust differentiation strategies capable of driving human EE cell differentiation is a critical step towards understanding these essential cells and the development of cell-based therapeutics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author J.M.K. holds equity in Frequency Therapeutics, a company that has an option to license IP generated by J.M.K. and that may benefit financially if the IP is licensed and further validated. Also, J.M.K. has been a paid consultant and/or equity holder for multiple companies (listed here
Figures




References
-
- Posovszky C. Development and anatomy of the enteroendocrine system in humans. Endocr. Dev. 2017;32:20–37. - PubMed
-
- Furness JB, Rivera LR, Cho HJ, Bravo DM, Callaghan B. The gut as a sensory organ. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013;10:729–740. - PubMed
-
- El-Salhy M, Hausken T, Gilja OH, Hatlebakk JG. The possible role of gastrointestinal endocrine cells in the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;11:139–148. - PubMed
-
- Worthington JJ, Reimann F, Gribble FM. Enteroendocrine cells-sensory sentinels of the intestinal environment and orchestrators of mucosal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2018;11:3–20. - PubMed
-
- Holst JJ, Vilsboll T, Deacon CF. The incretin system and its role in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2009;297:127–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

