Tumor infiltrating lymphocyte stratification of prognostic staging of early-stage triple negative breast cancer
- PMID: 35017545
- PMCID: PMC8752727
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-021-00362-1
Tumor infiltrating lymphocyte stratification of prognostic staging of early-stage triple negative breast cancer
Abstract
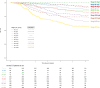
The importance of integrating biomarkers into the TNM staging has been emphasized in the 8th Edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Staging system. In a pooled analysis of 2148 TNBC-patients in the adjuvant setting, TILs are found to strongly up and downstage traditional pathological-staging in the Pathological and Clinical Prognostic Stage Groups from the AJJC 8th edition Cancer Staging System. This suggest that clinical and research studies on TNBC should take TILs into account in addition to stage, as for example patients with stage II TNBC and high TILs have a better outcome than patients with stage I and low TILs.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.L. receives research funding to her institution from Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Merck, Puma Biotechnology, Eli Lilly, Nektar Therapeutics Astra Zeneca, Roche-Genentech and Seattle Genetics. S.L. has acted as consultant (not compensated) to Seattle Genetics, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Merck, AstraZeneca and Roche-Genentech. S.L. has acted as consultant (paid to her institution) to Aduro Biotech, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche-Genentech, Astra Zeneca, Silverback Therapeutics, G1 Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, PUMA Biotechnologies, Seattle Genetics and Bristol Meyers Squibb. RS reports non-financial support from Merck and Bristol Myers Squibb; research support from Merck, Puma Biotechnology, and Roche; and personal fees from Roche for an advisory board related to a trial-research project. S.D. has received honorarium as a member of the scientific advisory board of Lytix Biopharma, and ad hoc consulting for Ono Pharmaceuticals. M.P. is a Scientific Board Member of Oncolytics. M.P. has acted as a consultant (compensated) to AstraZeneca, Camel-IDS/Precirix, Gilead, Immunomedics, Lilly, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Odonate, Pfizer, Roche-Genentech, Seattle Genetics, Immutep, Seagen, NBE Therapeutics, Frame Therapeutics. M.P. receives research funding to her institution from AstraZeneca, Immunomedics, Lilly, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Radius, Roche-Genentech, Servier, Synthon. E.M. has acted as a consultant (compensated) to Pierre Fabre, Genomic Health and Eisai. E.M. has received funding for travel expenses and/or accommodation from Celgene, Roche, Eisai, Mylan and Pfizer. C.D. reports stock and other ownership interests from Sividon Diagnostics (unitl 2016), honoraria from Novartis and Roche. C.D. has acted as a consultant (compensated) to MSD Oncology, Daiichi Sankyo, Molecular Health, Astra Zeneca, merck. C.D. receives research funding (to institution) from Myriad Genetics and Roche. C.D. reports patents, royalties and/or other intellectual property from VMScope digital pathology software, patent applications WO2015114146A1 and WO2010076322A1(therapy response) and WO2020109570A1 (cancer immunotherapy). C.D. has received funding for travel expenses and/or accommodation from Roche. H.J. is the Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board at Orion Pharma and at Neutron Therapeutics Ltd. S.M. reports fees outside the submitted work from statistical advice (IDDI, Janssen Cilag, Amaris, Roche) and from data and safety monitoring membership of clinical trials (Hexal, Steba, IQVIA, Sensorion, Biophytis, Servier, Yuhan. F.A. received research funding and served as speaker / advisor (compensated to the hospital) for Roche, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly. S.A. has uncompensated consulting or advisory roles with Bristol Meyers Squibb, Genentech, and Merck as well as research funding to her institution from Amgen, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Genentech, Merck and Novartis. M.V.D. reports personal fees for consultancy/advisory from Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Novartis, Genomic Health. MLT reports honorarium/expertise from Roche, Roche Diagnostics, MSD, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo. P.L.K.L. has received honorarium as member of advisory board of Bristol Myers Squibb and has received compensation for traveling from Sanofi. PAF reports honoraria from AstraZeneca and Novartis and travel support from Pfizer and Ipsen. The remaining authors declare competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

