Three cases of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma evaluated using conventional and contrast-enhanced ultrasound: Case reports
- PMID: 35018654
- PMCID: PMC9540860
- DOI: 10.1002/jcu.23141
Three cases of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma evaluated using conventional and contrast-enhanced ultrasound: Case reports
Abstract
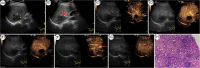
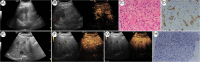
Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEHE) is a very rare vascular endothelial cell tumor, which lacks typical clinical manifestations and specificity of imaging features. Whether the background of fatty liver and the difference in Contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) characteristics between large and small lesions has not been well defined. In this case reports, we described the ultrasound image features of three patients with HEHE. These three patients with HEHE have certain similar characteristics of conventional ultrasound and CEUS. CEUS imaging features include large nodules show earlier perfusion than liver parenchyma, with rim-enhancement, nonenhancing regions in the center, while small nodules show earlier perfusion than liver parenchyma, with hyperenhancement. All nodules show faster washout than hepatic parenchyma, showing heterogeneous hypoenhancement, and more washout lesions can be found in the PVP and LP. Conventional ultrasound and CEUS not only help to improve the diagnostic confidence of HEHE of rare liver tumors, but also can guide the biopsy area, making it easier to make accurate pathological diagnosis.
Keywords: contrast enhanced ultrasound; focal liver lesions; hemangioendothelioma; hepatic neoplasm; rare tumors.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by the above institutions. All author declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2023 Jun 20;31(6):589-593. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20230314-00114. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37400382 Chinese.
-
[Ultrasonographic Features of Hepatic Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma on B-mode and Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017 Jul;48(4):595-599. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017. PMID: 28752981 Chinese.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of histologically proven hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 May 21;22(19):4741-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4741. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27217705 Free PMC article.
-
The challenges of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: the diagnosis and current treatments of a problematic tumor.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Nov 30;19(1):449. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03354-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 39616351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: Pitfalls in the diagnosis on fine needle cytology and "small biopsy" and review of the literature.Pathol Res Pract. 2015 Sep;211(9):702-5. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Pathol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 26187370 Review.
References
-
- Zhang L, Chen X‐J, Lee J‐M, Lin S‐S. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: challenges in the preoperative diagnosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2018;34:659‐661. - PubMed
-
- Mehrabi A, Kashfi A, Fonouni H, et al. Primary malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a comprehensive review of the literature with emphasis on the surgical therapy. Cancer. 2006;107:2108‐2121. - PubMed
-
- Makhlouf HR, Ishak KG, Goodman ZD. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: a clinicopathologic study of 137 cases. Cancer. 1999;85:562‐582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

