The nucleolar δ isoform of adapter protein SH2B1 enhances morphological complexity and function of cultured neurons
- PMID: 35019135
- PMCID: PMC8918807
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.259179
The nucleolar δ isoform of adapter protein SH2B1 enhances morphological complexity and function of cultured neurons
Abstract
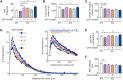
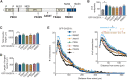
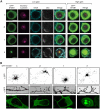
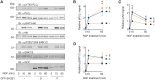
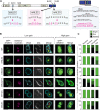
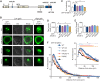
The adapter protein SH2B1 is recruited to neurotrophin receptors, including TrkB (also known as NTRK2), the receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Herein, we demonstrate that the four alternatively spliced isoforms of SH2B1 (SH2B1α-SH2B1δ) are important determinants of neuronal architecture and neurotrophin-induced gene expression. Primary hippocampal neurons from Sh2b1-/- [knockout (KO)] mice exhibit decreased neurite complexity and length, and BDNF-induced expression of the synapse-related immediate early genes Egr1 and Arc. Reintroduction of each SH2B1 isoform into KO neurons increases neurite complexity; the brain-specific δ isoform also increases total neurite length. Human obesity-associated variants, when expressed in SH2B1δ, alter neurite complexity, suggesting that a decrease or increase in neurite branching may have deleterious effects that contribute to the severe childhood obesity and neurobehavioral abnormalities associated with these variants. Surprisingly, in contrast to SH2B1α, SH2B1β and SH2B1γ, which localize primarily in the cytoplasm and plasma membrane, SH2B1δ resides primarily in nucleoli. Some SH2B1δ is also present in the plasma membrane and nucleus. Nucleolar localization, driven by two highly basic regions unique to SH2B1δ, is required for SH2B1δ to maximally increase neurite complexity and BDNF-induced expression of Egr1, Arc and FosL1.
Keywords: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Hippocampal neurons; Immediate early genes; Obesity; Protein isoforms; Signal-transducing adapter proteins.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alder, J., Thakker-Varia, S., Bangasser, D. A., Kuroiwa, M., Plummer, M. R., Shors, T. J. and Black, I. B. (2003). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced gene expression reveals novel actions of VGF in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 23, 10800-10808. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-34-10800.2003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, L., Maures, T. J., Jin, H., Huo, J. S., Rabbani, S. A., Schwartz, J. and Carter-Su, C. (2008). SH2B1β (SH2-Bβ) enhances expression of a subset of nerve growth factor-regulated genes important for neuronal differentiation including genes encoding uPAR and MMP3/10. Mol. Endocrinol. 22, 454-476. 10.1210/me.2007-0384 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

