Eliminating Explicit and Implicit Biases in Health Care: Evidence and Research Needs
- PMID: 35020445
- PMCID: PMC9172268
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-052620-103528
Eliminating Explicit and Implicit Biases in Health Care: Evidence and Research Needs
Abstract
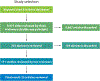
Health care providers hold negative explicit and implicit biases against marginalized groups of people such as racial and ethnic minoritized populations. These biases permeate the health care system and affect patients via patient-clinician communication, clinical decision making, and institutionalized practices. Addressing bias remains a fundamental professional responsibility of those accountable for the health and wellness of our populations. Current interventions include instruction on the existence and harmful role of bias in perpetuating health disparities, as well as skills training for the management of bias. These interventions can raise awareness of provider bias and engage health care providers in establishing egalitarian goals for care delivery, but these changes are not sustained, and the interventions have not demonstrated change in behavior in the clinical or learning environment. Unfortunately, the efficacy of these interventions may be hampered by health care providers' work and learning environments, which are rife with discriminatory practices that sustain the very biases US health care professions are seeking to diminish. We offer a conceptual model demonstrating that provider-level implicit bias interventions should be accompanied by interventions that systemically change structures inside and outside the health care system if the country is to succeed in influencing biases and reducing health inequities.
Keywords: bias; disparity; equity; racism.
Figures
References
-
- AAMC (Assoc. Am. Med. Coll.). Figure 2. Percentage of applicants to U.S. medical schools by race/ethnicity (alone), academic year 2018–2019. Washington, DC: AAMC. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/interactive-data/figure-2-pe...
-
- Amutah C, Greenidge K, Mante A, Munyikwa M, Surya SL, et al. 2021. Misrepresenting race—the role of medical schools in propagating physician bias. N. Engl. J. Med 384:872–78 - PubMed
-
- Andreychik M, Gill M. 2012. Do negative implicit associations indicate negative attitudes? Social explanations moderate whether ostensible “negative” associations are prejudice-based or empathy-based. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol 48:1082–93
-
- Axt JR, Ebersole CR, Nosek BA. 2014. The rules of implicit evaluation by race, religion, and age. Psychol. Sci 25:1804–15 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

