Systematic review of the efficacy, effectiveness and impact of high-valency pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on otitis media
- PMID: 35020530
- PMCID: PMC8973322
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2021.2013693
Systematic review of the efficacy, effectiveness and impact of high-valency pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on otitis media
Abstract
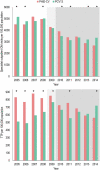
Otitis media (OM) is a common disease of childhood and available pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs), with different compositions, could have different impact on OM reduction. This systematic literature review evaluated available data describing the efficacy, effectiveness, and impact of 10-valent pneumococcal Haemophilus influenzae protein D conjugate vaccine (PHiD-CV) and 13-valent PCV (PCV13) on OM outcomes. Statistically significant reductions in all-cause and complicated OM, tympanostomy tube placement and OM-related hospitalizations were consistently observed after the introduction of PHiD-CV and PCV13. Impact studies with data in children <2 years of age using PCV13 report 47-51% and PHiD-CV 34-43% reduction of all-cause OM (primary care, outpatient, ambulatory, emergency department visits) compared to periods before PCV introduction. When the impact of both vaccines is assessed in comparable settings, some studies suggest PHiD-CV may offer better protection against some OM outcomes. Well-designed, head-to-head comparisons are needed to better understand the differences and guide vaccination policies.
Keywords: effectiveness; impact; incidence; otitis media; pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; systematic literature review; vaccine.
Plain language summary
Plain Language SummaryWhat is the context?Pneumococcal vaccines are highly effective in preventing pneumonia and meningitis in children. The two main pneumococcal vaccines are PHiD-CV (Synflorix, GSK) and PCV13 (Prevenar 13, Pfizer). Both vaccines have been shown to provide protection against otitis media despite differing in their composition.However, it is currently unknown if both vaccines confer similar level of protection against otitis media.What is new?We conducted a literature review to evaluate the effects of PHiD-CV and PCV13 on otitis media.From 33 articles, we found that:‡Both vaccines were effective in reducing doctor visits for otitis media as well as the number of severe cases and cases requiring hospitalization.‡Four studies suggested a higher level of protection provided by PHiD-CV compared to PCV13, although more data is needed to confirm this finding. What is the impact?Available information shows that PHiD-CV and PCV13 are effective in preventing a proportion of otitis media during childhood.Given the remaining substantial burden associated with the disease and the related significant usage of antibiotics, the development of improved vaccines with higher impact on otitis media would be welcome.
Conflict of interest statement
P Izurieta, M Scherbakov, J Nieto Guevara, V Vetter, and L Soumahoro are employees of the GSK group of companies and declare financial (including shares) and non-financial relationships and activities.
Figures





References
-
- Tin Tin Htar M, van Den Biggelaar AHJ, Sings H, Ferreira G, Moffatt M, Hall-Murray C, Verstraeten T, Gessner BD, Schmitt H-J, Jodar L, et al. The impact of routine childhood immunization with higher-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on antimicrobial-resistant pneumococcal diseases and carriage: a systematic literature review. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019;18(10):1069–18. doi:10.1080/14760584.2019.1676155. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alicino C, Paganino C, Orsi A, Astengo M, Trucchi C, Icardi G, Ansaldi F. The impact of 10-valent and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on hospitalization for pneumonia in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Vaccine. 2017;35:5776–85. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.09.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
