GSDMB is increased in IBD and regulates epithelial restitution/repair independent of pyroptosis
- PMID: 35021065
- PMCID: PMC8879997
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.024
GSDMB is increased in IBD and regulates epithelial restitution/repair independent of pyroptosis
Erratum in
-
GSDMB is increased in IBD and regulates epithelial restitution/repair independent of pyroptosis.Cell. 2024 Feb 15;187(4):1011-1015. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.010. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38364781 No abstract available.
Abstract
Gasdermins are a family of structurally related proteins originally described for their role in pyroptosis. Gasdermin B (GSDMB) is currently the least studied, and while its association with genetic susceptibility to chronic mucosal inflammatory disorders is well established, little is known about its functional relevance during active disease states. Herein, we report increased GSDMB in inflammatory bowel disease, with single-cell analysis identifying epithelial specificity to inflamed colonocytes/crypt top colonocytes. Surprisingly, mechanistic experiments and transcriptome profiling reveal lack of inherent GSDMB-dependent pyroptosis in activated epithelial cells and organoids but instead point to increased proliferation and migration during in vitro wound closure, which arrests in GSDMB-deficient cells that display hyper-adhesiveness and enhanced formation of vinculin-based focal adhesions dependent on PDGF-A-mediated FAK phosphorylation. Importantly, carriage of disease-associated GSDMB SNPs confers functional defects, disrupting epithelial restitution/repair, which, altogether, establishes GSDMB as a critical factor for restoration of epithelial barrier function and the resolution of inflammation.
Keywords: FAK; GSDMB; GSDMB genetic polymorphisms; Mtx; PDGFA; epithelial organoids; epithelial restitution and repair; focal adhesion kinase; gasdermin B; gasdermins; inflammatory bowel disease; intestinal epithelial cells; methotrexate; platelet-derived growth factor A; resolution of inflammation; single-cell RNA-seq; single-cell profiling.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

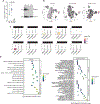
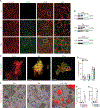
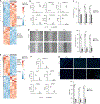
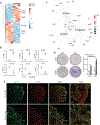
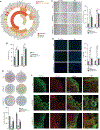
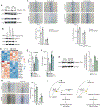
Comment in
-
The healing role of gasdermin B in IBD.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Mar;23(3):167. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00453-2. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35039678 No abstract available.
-
Gasdermin B in IBD and epithelial barrier repair.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;19(4):216. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00589-8. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35140367 No abstract available.
-
Novel pyroptosis-independent functions of gasdermins.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Apr 22;7(1):127. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00991-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35459858 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bartolomé RA, Barderas R, Torres S, Fernandez-Aceñero MJ, Mendes M, García-Foncillas J, Lopez-Lucendo M, Casal JI, 2014. Cadherin-17 interacts with α2β1 integrin to regulate cell proliferation and adhesion in colorectal cancer cells causing liver metastasis. Oncogene 33, 1658–1669. 10.1038/onc.2013.117 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI141350/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK091222/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD016164/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK097948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK108278/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK042191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S036377/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00008/7/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12010/7/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK126702/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T35 DK111373/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125293/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI089474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_MR/S025952/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R35 GM141603/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM086550/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK042191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK042191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA214300/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

