Alpha synuclein, the culprit in Parkinson disease, is required for normal immune function
- PMID: 35021075
- PMCID: PMC10258816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110090
Alpha synuclein, the culprit in Parkinson disease, is required for normal immune function
Abstract
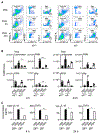
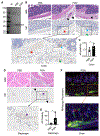
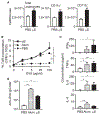
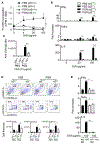
Alpha-synuclein (αS) is causally involved in the development of Parkinson disease (PD); however, its role in normal vertebrate physiology has remained unknown. Recent studies demonstrate that αS is induced by noroviral infection in the enteric nervous system of children and protects mice against lethal neurotropic viral infection. Additionally, αS is a potent chemotactic activator of phagocytes. In this report, using both wild-type and αS knockout mice, we show that αS is a critical mediator of inflammatory and immune responses. αS is required for the development of a normal inflammatory response to bacterial peptidoglycan introduced into the peritoneal cavity as well as antigen-specific and T cell responses following intraperitoneal immunization. Furthermore, we show that neural cells are the sources of αS required for immune competence. Our report supports the hypothesis that αS accumulates within the nervous system of PD individuals because of an inflammatory/immune response.
Keywords: Parkinson disease; alarmins; alpha-synuclein; dendritic cells; immune response; immunization; inflammation; macrophage; peritoneal cavity; αS.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Akira S, and Takeda K (2004). Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol 4, 499–511. - PubMed
-
- Barbour R, Kling K, Anderson JP, Banducci K, Cole T, Diep L, Fox M, Goldstein JM, Soriano F, Seubert P, and Chilcote TJ (2008). Red blood cells are the major source of alpha-synuclein in blood. Neurodegener. Dis 5, 55–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

