Endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy versus laparoscopic appendectomy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis
- PMID: 35021234
- PMCID: PMC9329065
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1737-6381
Endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy versus laparoscopic appendectomy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy (ERAT) is a new and minimally invasive technique for the treatment of acute appendicitis. This study aimed to assess the efficacy and clinical outcomes of ERAT versus laparoscopic appendectomy for patients with uncomplicated acute appendicitis.
Methods: We adopted propensity score matching (1:1) to compare ERAT and laparoscopic appendectomy in patients with uncomplicated acute appendicitis between April 2017 and March 2020. We reviewed 2880 patients with suspected acute appendicitis, of whom 422 patients with uncomplicated acute appendicitis met the matching criteria (ERAT 79; laparoscopic appendectomy 343), yielding 78 pairs of patients.
Results: The rate of curative treatment within 1 year after ERAT was 92.1 % (95 % confidence interval [CI] 83.8 % to 96.3 %). The percentage of patients recording visual analog scale values of ≤ 3 for pain at 6 hours after treatment was 94.7 % (95 %CI 87.2 % to 97.9 %) in the ERAT group, which was significantly higher than that in the laparoscopic appendectomy group (83.3 %; 95 %CI 73.5 % to 90.0 %). Median procedure time and median hospital length of stay were significantly lower in the ERAT group compared with the laparoscopic appendectomy group. At 1 year, the median recurrence time was 50 days (interquartile range 25-127) in the ERAT group. The overall adverse event rate was 24.4 % (95 %CI 14.8 % to 33.9 %) in the laparoscopic appendectomy group and 18.4 % (95 %CI 9.7 % to 27.1 %) in the ERAT group, with no significant difference between the two groups.
Conclusion: ERAT was a technically feasible method of treating uncomplicated acute appendicitis compared with laparoscopic appendectomy.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
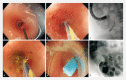


Comment in
-
Endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy: a starting point for a change of perspective in treating acute appendicitis (and beyond).Endoscopy. 2022 Aug;54(8):755-756. doi: 10.1055/a-1759-2859. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Endoscopy. 2022. PMID: 35255524 No abstract available.
-
Author commentary on Baohong Yang et al.Endoscopy. 2022 Aug;54(8):v28. doi: 10.1055/a-1745-7847. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Endoscopy. 2022. PMID: 35896156 No abstract available.
References
-
- Harris C W. Abraham Groves of Fergus: the first elective appendectomy? Can J Surg. 1961;4:405–410. - PubMed
-
- Semm K. Endoscopic appendectomy. Endoscopy. 1983;15:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Poprom N, Numthavaj P, Wilasrusmee C et al. The efficacy of antibiotic treatment versus surgical treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. Am J Surg. 2019;218:192–200. - PubMed
-
- Liu B R, Song J T, Han F Y et al. Endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy: a pilot minimally invasive technique (with videos) Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76:862–866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

