Infectious Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Virus in Symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outpatients: Host, Disease, and Viral Correlates
- PMID: 35022711
- PMCID: PMC9402664
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciab968
Infectious Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Virus in Symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outpatients: Host, Disease, and Viral Correlates
Abstract
Background: Although severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infectious virus isolation in outpatients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been associated with viral RNA levels and symptom duration, little is known about the host, disease, and viral determinants of infectious virus detection.
Methods: COVID-19 adult outpatients were enrolled within 7 days of symptom onset. Clinical symptoms were recorded via patient diary. Nasopharyngeal swabs were collected to quantitate SARS-CoV-2 RNA by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and for infectious virus isolation in Vero E6-cells. SARS-CoV-2 antibodies were measured in serum using a validated ELISA assay.
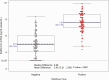
Results: Among 204 participants with mild-to-moderate symptomatic COVID-19, the median nasopharyngeal viral RNA was 6.5 (interquartile range [IQR] 4.7-7.6 log10 copies/mL), and 26% had detectable SARS-CoV-2 antibodies (immunoglobulin (Ig)A, IgM, IgG, and/or total Ig) at baseline. Infectious virus was recovered in 7% of participants with SARS-CoV-2 antibodies compared to 58% of participants without antibodies (prevalence ratio [PR] = 0.12, 95% confidence interval [CI]: .04, .36; P = .00016). Infectious virus isolation was also associated with higher levels of viral RNA (mean RNA difference +2.6 log10, 95% CI: 2.2, 3.0; P < .0001) and fewer days since symptom onset (PR = 0.79, 95% CI: .71, .88 per day; P < .0001).
Conclusions: The presence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies is strongly associated with clearance of infectious virus. Seropositivity and viral RNA levels are likely more reliable markers of infectious virus clearance than subjective measure of COVID-19 symptom duration. Virus-targeted treatment and prevention strategies should be administered as early as possible and ideally before seroconversion.
Clinical trials registration: NCT04405570.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; infectious virus; outpatient; serostatus.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Update of
-
Infectious SARS-CoV-2 Virus in Symptomatic COVID-19 Outpatients: Host, Disease, and Viral Correlates.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Jun 25:2021.05.28.21258011. doi: 10.1101/2021.05.28.21258011. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 24;75(1):e1028-e1036. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab968. PMID: 34100024 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 27 October 2021.
-
- CDC. Interim guidance on duration of isolation and precautions for adults with COVID-19. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/duration-isolation.html. Accessed 12 April 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

