Population Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Optimization of Gentamicin in Critically Ill Patients Undergoing Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
- PMID: 35023902
- PMCID: PMC8747548
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S343385
Population Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Optimization of Gentamicin in Critically Ill Patients Undergoing Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Appropriate gentamicin dosing in continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) patients remains undefined. This study aimed to develop a population pharmacokinetic (PK) model of gentamicin in CRRT patients and to infer the optimal dosing regimen for gentamicin.
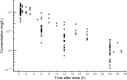
Methods: Fourteen CRRT patients dosed with gentamicin were included to establish a population PK model to characterize the variabilities and influential covariates of gentamicin. The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) target attainment and risk of toxicity for different combinations of gentamicin regimens (3-7 mg/kg q24h) and CRRT effluent doses (30-50 mL/h/kg) were evaluated by Monte Carlo simulation. The probability of target attainment (PTA) was determined for the PK/PD indices of the ratio of drug peak concentration/minimum inhibitory concentration (Cmax/MIC > 10) and the ratio of area under the drug concentration-time curve/MIC over 24 h (AUC0-24h/MIC > 100), and the risk of toxicity was estimated by drug trough concentration thresholds (1 and 2 mg/L).
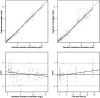
Results: A one-compartment model adequately described the PK characteristics of gentamicin. Covariates including body weight, age, gender, and CRRT modality did not influence the PK parameters of gentamicin based on our dataset. All studied gentamicin regimens failed to achieve satisfactory PTAs for pathogens with an MIC ≥2 mg/L. A good balance of PK/PD target attainment and risk of toxicity (>2 mg/L) was achieved under 7 mg/kg gentamicin q24h and 40 mL/kg/h CRRT dose for an MIC ≤1 mg/L. CRRT dose intensity had a significant impact on the target attainment of AUC0-24h/MIC >100 and risk of toxicity.
Conclusion: A combination of 7 mg/kg gentamicin q24h and 40 mL/kg/h CRRT dose might be considered as a starting treatment option for CRRT patients, and drug monitoring is required to manage toxicity.
Keywords: CRRT; critically ill; gentamicin; population pharmacokinetics.
© 2022 He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Garnacho-Montero J, Garcia-Garmendia JL, Barrero-Almodovar A, Jimenez-Jimenez FJ, Perez-Paredes C, Ortiz-Leyba C. Impact of adequate empirical antibiotic therapy on the outcome of patients admitted to the intensive care unit with sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2003;31(12):2742–2751. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000098031.24329.10 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

