Hospital admission for COVID-19 pneumonitis - long-term impairment in quality of life and lung function
- PMID: 35024101
- PMCID: PMC8745367
- DOI: 10.1080/20018525.2021.2024735
Hospital admission for COVID-19 pneumonitis - long-term impairment in quality of life and lung function
Abstract
Background and aim: Knowledge of long-term consequences of severe COVID-19 pneumonitis is of outmost importance. Our aim was, therefore, to assess the long-term impact on quality of life and lung function in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19.
Methods: All patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonitis at Copenhagen University Hospital-Hvidovre, Denmark, were invited to participate in the study 4-5 months after discharge. Of the 160 invited 128 responded positively (80%). Medical history and symptoms were assessed, and patients rated impact on quality of life and functional status with EuroQol-5D-5L and Post Covid Functional Scale. Lung function was assessed by dynamic spirometry and measurement of diffusing capacity.
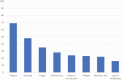
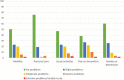
Results: Fatigue, dyspnea, cough and cognitive dysfunction were the most common symptoms. Of 128 patients, 85% had at least one symptom, and 51% reported two or more symptoms. Self-rated Quality of life was impaired assessed by EuroQol 5D-5L, with dimensions 'Pain or discomfort' (61%) and 'Usual activities' (54%) mostly affected. Functional status was significantly worse than before COVID-19 assessed by Post-COVID Functional Scale. Among lung function parameters, diffusing capacity was most affected, with 45% having diffusing capacity < 80% of predicted.
Conclusion: Fatigue, respiratory symptoms and cognitive symptoms are highly common months after hospitalization for severe COVID-19. Compared to pre-COVID-19, functional status and usual activities continued to be impaired. In line with this, almost half of the patients were found to have impaired diffusing capacity.
Keywords: COVID-19; health-related quality of life; long term follow up; pulmonary function; sequelae.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed H, Patel K, Greenwood DC, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreaks after hospitalisation or ICU admission: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2020. May 31;52(5):jrm00063. PMID: 32449782. - PubMed
-
- Ong KC, Ng AW, Lee LS, et al. Pulmonary function and exercise capacity in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Eur Respir J. 2004. Sep;24(3):436–442. PMID: 15358703. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
