Toward Cumulative Cognitive Science: A Comparison of Meta-Analysis, Mega-Analysis, and Hybrid Approaches
- PMID: 35024529
- PMCID: PMC8746126
- DOI: 10.1162/opmi_a_00048
Toward Cumulative Cognitive Science: A Comparison of Meta-Analysis, Mega-Analysis, and Hybrid Approaches
Abstract
There is increasing interest in cumulative approaches to science, in which instead of analyzing the results of individual papers separately, we integrate information qualitatively or quantitatively. One such approach is meta-analysis, which has over 50 years of literature supporting its usefulness, and is becoming more common in cognitive science. However, changes in technical possibilities by the widespread use of Python and R make it easier to fit more complex models, and even simulate missing data. Here we recommend the use of mega-analyses (based on the aggregation of data sets collected by independent researchers) and hybrid meta- mega-analytic approaches, for cases where raw data are available for some studies. We illustrate the three approaches using a rich test-retest data set of infants' speech processing as well as synthetic data. We discuss advantages and disadvantages of the three approaches from the viewpoint of a cognitive scientist contemplating their use, and limitations of this article, to be addressed in future work.
Keywords: cumulative science; data simulation; fixed effects; mega-analyses; meta-analyses; open science; random effects.
© 2021 Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
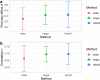
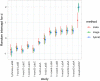
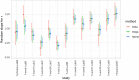
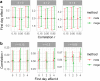
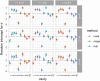
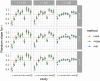
References
-
- Aust, F., & Barth, M. (2017). Papaja: Prepare reproducible APA journal articles with R Markdown. R package version 0.1.0.9997. GitHub. https://github.com/crsh/papaja
-
- Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B., & Walker, S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models Using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1). 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
-
- Baumer, B., & Udwin, D. (2015). R markdown. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, 7(3), 167–177. 10.1002/wics.1348 - DOI
-
- Bergmann, C., Tsuji, S., Piccinini, P. E., Lewis, M. L., Braginsky, M., Frank, M. C., & Cristia, A. (2018). Promoting replicability in developmental research through meta-analyses: Insights from language acquisition research. Child Development, 89(6), 1996–2009. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13079, PubMed: 29736962 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black, A., & Bergmann, C. (2017). Quantifying infants’ statistical word segmentation: A meta-analysis. In Gunzelmann G., Howes A., Tenbrink T., & Davelaar E. (Eds.), Proceedings of the 39th Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (pp. 124–129). Cognitive Science Society.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
