Neural regulations of the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 35024571
- PMCID: PMC8728107
- DOI: 10.1096/fba.2021-00066
Neural regulations of the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
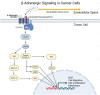
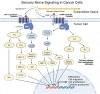
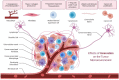
The identification of nerves in the tumor microenvironment has ushered in a new area of research in cancer biology. Numerous studies demonstrate the presence of various types of peripheral nerves (sympathetic, parasympathetic, sensory) within the tumor microenvironment; moreover, an increased density of nerves in the tumor microenvironment correlates with worse prognosis. In this review, we address the current understanding of nerve-mediated alterations of the tumor microenvironment and how they impact disease through a variety of processes, including direct nerve-cancer cell communication, alteration of the infiltrative immune population, and alteration of stromal components.
Keywords: cancer; immune escape; neuro‐immune communication; tumor innervation; tumor microenvironment.
© 2021 The Authors FASEB BioAdvances published by The Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Duechler M, Peczek L, Zuk K, Zalesna I, Jeziorski A, Czyz M. The heterogeneous immune microenvironment in breast cancer is affected by hypoxia‐related genes. Immunobiol. 2014;219(2):158‐165. - PubMed
-
- Balsamo M, Manzini C, Pietra G, et al. Hypoxia downregulates the expression of activating receptors involved in NK‐cell‐mediated target cell killing without affecting ADCC. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43(10):2756‐2764. - PubMed
-
- Liu B, Wei C. Hypoxia induces overexpression of CCL28 to recruit treg cells to enhance angiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2021;40(1):65‐74. - PubMed
-
- So T, Takenoyama M, Mizukami M, et al. Haplotype loss of HLA class I antigen as an escape mechanism from immune attack in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(13):5945‐5952. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
