Adding stress biomarkers to high-sensitivity cardiac troponin for rapid non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction rule-out protocols
- PMID: 35024819
- PMCID: PMC8929978
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuab124
Adding stress biomarkers to high-sensitivity cardiac troponin for rapid non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction rule-out protocols
Abstract
Aims: This study tested the hypothesis that combining stress-induced biomarkers (copeptin or glucose) with high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) increases diagnostic accuracy for non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) in patients presenting to the emergency department.
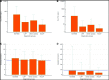
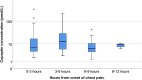
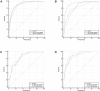
Methods and results: The ability to rule-out NSTEMI for combinations of baseline hs-cTnT or hs-cTnI with copeptin or glucose was compared with the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) hs-cTnT/I-only rule-out algorithms in two independent (one Norwegian and one international multicentre) diagnostic studies. Among 959 patients (median age 64 years, 60.5% male) with suspected NSTEMI in the Norwegian cohort, 13% had NSTEMI. Adding copeptin or glucose to hs-cTnT/I as a continuous variable did not improve discrimination as quantified by the area under the curve {e.g. hs-cTnT/copeptin 0.91 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.89-0.93] vs. hs-cTnT alone 0.91 (95% CI 0.89-0.93); hs-cTnI/copeptin 0.85 (95% CI 0.82-0.87) vs. hs-cTnI alone 0.93 (95% CI 0.91-0.95)}, nor did adding copeptin <9 mmol/L or glucose <5.6 mmol/L increase the sensitivity of the rule-out provided by hs-cTnT <5 ng/L or hs-cTnI <4 ng/L in patients presenting more than 3 h after chest pain onset (target population in the ESC-0 h-algorithm). The combination decreased rule-out efficacy significantly (both P < 0.01). These findings were confirmed among 1272 patients (median age 62 years, 69.3% male) with suspected NSTEMI in the international validation cohort, of which 20.7% had NSTEMI. A trend towards increased sensitivity for the hs-cTnT/I/copeptin combinations (97-100% vs. 91-97% for the ESC-0 h-rule-out cut-offs) was observed in the Norwegian cohort.
Conclusion: Adding copeptin or glucose to hs-cTnT/I did not increase diagnostic performance when compared with current ESC guideline hs-cTnT/I-only 0 h-algorithms.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Copeptin; Glucose; NSTEMI; NSTEMI rule-out; Stress biomarkers.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Multiple biomarkers for rapid rule-out of myocardial infarction: worth the added stress?Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2022 Mar 16;11(3):213-214. doi: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuac019. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2022. PMID: 35146506 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nørgaard B, Mogensen CB, Teglbjærg LS, Brabrand M, Lassen AT.. Diagnostic packages can be assigned accurately in emergency departments. A multi-centre cohort study. Dan Med J 2016;63:A5240. - PubMed
-
- Niska R, Bhuiya F, Xu J.. National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2007 emergency department summary. Natl Health Stat Report 2010;26:1–31. - PubMed
-
- Bjørnsen LP, Naess-Pleym LE, Dale J, Grenne B, Wiseth R.. Description of chest pain patients in a Norwegian emergency department. Scand Cardiovasc J 2019;53:28–34. - PubMed
-
- Keller T, Zeller T, Peetz D, Tzikas S, Roth A, Czyz E, Bickel C, Baldus S, Warnholtz A, Fröhlich M, Sinning CR, Eleftheriadis MS, Wild PS, Schnabel RB, Lubos E, Jachmann N, Genth-Zotz S, Post F, Nicaud V, Tiret L, Lackner KJ, Münzel TF, Blankenberg S.. Sensitive troponin I assay in early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 2009;361:868–877. - PubMed
-
- Collet J-P, Thiele H, Barbato E, Barthélémy O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, Dendale P, Dorobantu M, Edvardsen T, Folliguet T, Gale CP, Gilard M, Jobs A, Jüni P, Lambrinou E, Lewis BS, Mehilli J, Meliga E, Merkely B, Mueller C, Roffi M, Rutten FH, Sibbing D, Siontis GCM; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: the task force for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2020;42:1289–1367. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

