Interleukin-12 as an in situ cancer vaccine component: a review
- PMID: 35024897
- PMCID: PMC9276836
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-022-03144-1
Interleukin-12 as an in situ cancer vaccine component: a review
Abstract
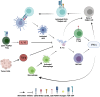
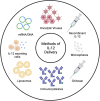
Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a type I cytokine involved in both innate and adaptive immunity that stimulates T and natural killer cell activity and induces interferon gamma production. IL-12 has been identified as a potential immunotherapeutic component for combinatorial cancer treatments. While IL-12 has successfully been used to treat a variety of cancers in mice, it was associated with toxicity when administered systemically in cancer patients. In this review, we discuss the research findings and progress of IL-12 used in combination with other cancer treatment modalities. We describe different methods of IL-12 delivery, both systemic and local, and ultimately highlight the potential of an in situ vaccination approach for minimizing toxicities and providing antitumor efficacy. This review offers a basis for pursuing an in situ vaccine approach that may eventually allow IL-12 to be more readily integrated as an immunotherapy into the clinical treatment of cancers.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; In situ cancer vaccine; Interleukin-12; Local delivery; Targeted delivery.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

