Immunostimulants for shrimp aquaculture: paving pathway towards shrimp sustainability
- PMID: 35025041
- PMCID: PMC8755978
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-18433-y
Immunostimulants for shrimp aquaculture: paving pathway towards shrimp sustainability
Abstract
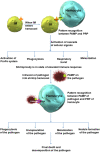
At present, food security is a matter of debate of global magnitude and fulfilling the feeding requirement of > 8 billion human populations by 2030 is one of the major concerns of the globe. Aquaculture plays a significant role to meet the global food requirement. Shrimp species such as Litopenaeus vannamei, Penaeus monodon, and Macrobrachium rosenbergii are among the most popular food commodities worldwide. As per Global Outlook for Aquaculture Leadership survey, disease outbreaks have been a matter of concern from the past many decades regarding the shrimp aquaculture production. Among the past disease outbreaks, white spot disease caused by the white spot syndrome virus is considered to be one of the most devastating ones that caused colossal losses to the shrimp industry. Since the virus is highly contagious, it spreads gregariously among the shrimp population; hence, practicing proper sanitization practices is crucial in order to have disease-free shrimps. Additionally, in order to control the disease, antibiotics were used that further leads to bioaccumulation and biomagnification of antibiotics in several food webs. The bioaccumulation of the toxic residues in the food webs further adversely affected human too. Recently, immunostimulants/antivirals were used as an alternative to antibiotics. They were found to enhance the immune system of shrimps in eco-friendly manner. In context to this, the present paper presents a critical review on the immunostimulants available from plants, animals, and chemicals against WSSV in shrimps. Looking into this scenario, maintaining proper sanitation procedures in conjunction with the employment of immunostimulants may be a viable approach for preserving shrimp aquaculture across the globe.
Keywords: Antivirals; Eco-friendly; Food security; Immunostimulants; Shrimp sustainable aquaculture; White spot disease; White spot syndrome virus.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Aguirre-Guzmán G, Sánchez-Martínez JG, Pérez-Castañeda R, et al. Pathogenicity and infection route of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in American white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J World Aquac Soc. 2010;41:464–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-7345.2010.00388.x. - DOI
-
- Ancieta-Probstl D, Smullen R, Barnes A. Enhancing growth performance of shrimp with nucleotide supplemented diets. Aquac Asiapacific. 2005;1:26–28.
-
- Apines-Amar MJS, Amar EC. 3. Use of immunostimulants in shrimp culture: an update. Res Signpost. 2015;37661:45–71.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

