Androgen receptor signaling promotes Treg suppressive function during allergic airway inflammation
- PMID: 35025767
- PMCID: PMC8843736
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI153397
Androgen receptor signaling promotes Treg suppressive function during allergic airway inflammation
Abstract
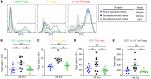
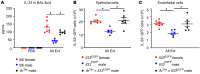
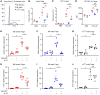
Women have higher prevalence of asthma compared with men. In asthma, allergic airway inflammation is initiated by IL-33 signaling through ST2, leading to increased IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 production and eosinophil infiltration. Foxp3+ Tregs suppress and ST2+ Tregs promote allergic airway inflammation. Clinical studies showed that the androgen dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) reduced asthma symptoms in patients, and mouse studies showed that androgen receptor (AR) signaling decreased allergic airway inflammation. Yet the impact of AR signaling on lung Tregs remains unclear. Using AR-deficient and Foxp3 fate-mapping mice, we determined that AR signaling increased Treg suppression during Alternaria extract (Alt Ext; allergen) challenge by stabilizing Foxp3+ Tregs and limiting the number of ST2+ ex-Tregs and IL-13+ Th2 cells and ex-Tregs. AR signaling also decreased Alt Ext-induced ST2+ Tregs in mice by limiting expression of Gata2, a transcription factor for ST2, and by decreasing Alt Ext-induced IL-33 production from murine airway epithelial cells. We confirmed our findings in human cells where 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT), an androgen, decreased IL-33-induced ST2 expression in lung Tregs and decreased Alt Ext-induced IL-33 secretion in human bronchial epithelial cells. Our findings showed that AR signaling stabilized Treg suppressive function, providing a mechanism for the sex difference in asthma.
Keywords: Asthma; Inflammation; Pulmonology; Sex hormones; T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 HL150783/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126176/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122554/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL136888/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI124456/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI111820/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004299/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- I01 BX002288/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- T32 GM007347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL159594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136664/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI095227/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI143005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI145265/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

