Waning antibody levels after COVID-19 vaccination with mRNA Comirnaty and inactivated CoronaVac vaccines in blood donors, Hong Kong, April 2020 to October 2021
- PMID: 35027105
- PMCID: PMC8759113
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.2.2101197
Waning antibody levels after COVID-19 vaccination with mRNA Comirnaty and inactivated CoronaVac vaccines in blood donors, Hong Kong, April 2020 to October 2021
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Euro Surveill. 2022;27(2).Euro Surveill. 2022 Jan;27(3):220120e. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.27.3.220120e. Euro Surveill. 2022. PMID: 35057903 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
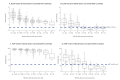
The mRNA vaccine Comirnaty and the inactivated vaccine CoronaVac are both available in Hong Kong's COVID-19 vaccination programme. We observed waning antibody levels in 850 fully vaccinated (at least 14 days passed after second dose) blood donors using ELISA and surrogate virus neutralisation test. The Comirnaty-vaccinated group's (n = 593) antibody levels remained over the ELISA and sVNT positive cut-offs within the first 6 months. The CoronaVac-vaccinated group's (n = 257) median antibody levels began to fall below the cut-offs 4 months after vaccination.
Keywords: BNT162b2; COVID-19; CoronaVac; SARS-CoV-2; antibody; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- The Government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. Hong Kong vaccination dashboard. Hong Kong: The Government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region; 2021. [Accessed: 5 Dec 2021]. Available from: https://www.covidvaccine.gov.hk/en/dashboard/
-
- European Medicines Agency. COVID-19 vaccines: under evaluation. Amsterdam: EMA; 2022. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/public-health-thr....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous