Cysteine oxidation of copper transporter CTR1 drives VEGFR2 signalling and angiogenesis
- PMID: 35027734
- PMCID: PMC8851982
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-021-00822-7
Cysteine oxidation of copper transporter CTR1 drives VEGFR2 signalling and angiogenesis
Abstract
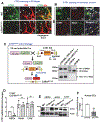
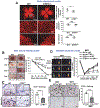
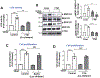
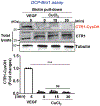
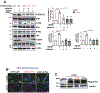
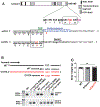
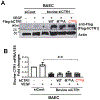
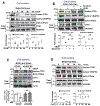
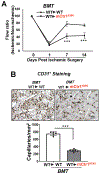
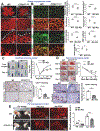
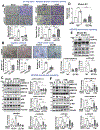
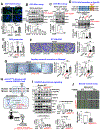
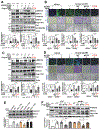
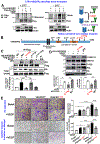
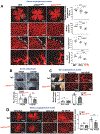
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2 (VEGFR2, also known as KDR and FLK1) signalling in endothelial cells (ECs) is essential for developmental and reparative angiogenesis. Reactive oxygen species and copper (Cu) are also involved in these processes. However, their inter-relationship is poorly understood. Evidence of the role of the endothelial Cu importer CTR1 (also known as SLC31A1) in VEGFR2 signalling and angiogenesis in vivo is lacking. Here, we show that CTR1 functions as a redox sensor to promote angiogenesis in ECs. CTR1-depleted ECs showed reduced VEGF-induced VEGFR2 signalling and angiogenic responses. Mechanistically, CTR1 was rapidly sulfenylated at Cys189 at its cytosolic C terminus after stimulation with VEGF, which induced CTR1-VEGFR2 disulfide bond formation and their co-internalization to early endosomes, driving sustained VEGFR2 signalling. In vivo, EC-specific Ctr1-deficient mice or CRISPR-Cas9-generated redox-dead Ctr1(C187A)-knockin mutant mice had impaired developmental and reparative angiogenesis. Thus, oxidation of CTR1 at Cys189 promotes VEGFR2 internalization and signalling to enhance angiogenesis. Our study uncovers an important mechanism for sensing reactive oxygen species through CTR1 to drive neovascularization.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures
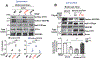

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL160014/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL124248/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135584/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003221/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL116976/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX005228/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- L40 HL120308/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133613/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 EY029373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY031631/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY029318/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY030500/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EY032265/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM135179/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011766/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 EY029373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147550/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001233/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL070187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001232/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

