Systematic Pan-Cancer Analysis of KLRB1 with Prognostic Value and Immunological Activity across Human Tumors
- PMID: 35028320
- PMCID: PMC8749375
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5254911
Systematic Pan-Cancer Analysis of KLRB1 with Prognostic Value and Immunological Activity across Human Tumors
Abstract
Introduction: KLRB1 is a gene encoding CD161 expressed in NK cells and some T cell subsets. At present, KLRB1 is believed to affect tumorigenesis and development by regulating the cytotoxicity of NK cells in several cancers. However, there is a lack of systematic reviews of KLRB1 in a variety of malignancies.
Objectives: Hence, our research is aimed at providing a relatively comprehensive understanding of the role of KLRB1 in different types of cancer, paving the way for further research on the molecular mechanism and immunotherapy potential of KLRB1.
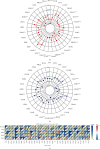
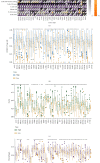
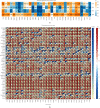
Methods: In this study, we used relevant public databases, including TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas), GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus), CCLE (Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia), GTEx (Genotype Tissue-Expression), and HPA (Human Protein Atlas), to perform a pan-cancer analysis of KLRB1 across 33 types of cancer. We explored the potential molecular mechanism of KLRB1 in clinical prognosis and tumor immunity from the aspects of gene expression, survival status, clinical phenotype, immune infiltration, immunotherapy response, and chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity.
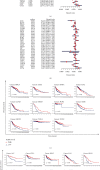
Results: KLRB1 was downregulated in 13 cancers while upregulated in kidney cancer. Patients with high expression of KLRB1 have a better prognosis in most types of cancer. Moreover, the KLRB1 expression level is related to TMB and MSI and related to various immune signatures of tumor. The expression of KLRB1 can affect tumor immune cell infiltration. KLRB1 expression level can also affect the sensitivity of chemotherapy drugs.
Conclusions: KLRB1 may be a prognostic and immunological biomarker across tumors. At the same time, KLRB1 expression can reflect the sensitivity of cancer patients to chemotherapy drugs. KLRB1 may become a new target for immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2022 Xin Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Our study is based on open source data; users can download relevant data for free. The patients in the database have obtained ethical approval, so there are no ethical issues and other conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lanier L. L., Chang C., Phillips J. H. Human NKR-P1A. A disulfide-linked homodimer of the C-type lectin superfamily expressed by a subset of NK and T lymphocytes. Journal of immunology, virus research and experimental chemotherapy . 1994;153(6):2417–2428. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

