Potential of Withaferin-A, Withanone and Caffeic Acid Phenethyl ester as ATP-competitive inhibitors of BRAF: A bioinformatics study
- PMID: 35028596
- PMCID: PMC8714769
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2021.11.004
Potential of Withaferin-A, Withanone and Caffeic Acid Phenethyl ester as ATP-competitive inhibitors of BRAF: A bioinformatics study
Abstract
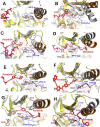
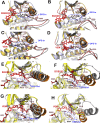
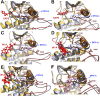
Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF) plays a significant role in regulating cell division and proliferation through MAPK/ERK pathway. The constitutive expression of wild-type BRAF (BRAFWT) and its mutant forms, especially V600E (BRAFV600E), has been linked to multiple cancers. Various synthetic drugs have been approved and are in clinical trials, but most of them are reported to become ineffective within a short duration. Therefore, combinational therapy involving multiple drugs are often recruited for cancer treatment. However, they lead to toxicity and adverse side effects. In this computational study, we have investigated three natural compounds, namely Withaferin-A (Wi-A), Withanone (Wi-N) and Caffeic Acid Phenethyl ester (CAPE) for anti-BRAFWT and anti-BRAFV600E activity. We found that these compounds could bind stably at ATP-binding site in both BRAFWT and BRAFV600E proteins. In-depth analysis revealed that these compounds maintained the active conformation of wild-type BRAF protein by inducing αC-helix-In, DFG-In, extended activation segment and well-aligned R-spine residues similar to already known drugs Vemurafenib (VEM), BGB283 and Ponatinib. In terms of binding energy, among the natural compounds, CAPE showed better affinity towards both wild-type and V600E mutant proteins than the other two compounds. These data suggested that CAPE, Wi-A and Wi-N have potential to block constitutive autophosphorylation of BRAF and hence warrant in vitro and in vivo experimental validation.
Keywords: ATP-Competitive inhibitors and cancer; BRAF; BRAF V600E mutant; Caffeic acid phenethyl ester; Withaferin-A; Withanone.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computational Insights into the Potential of Withaferin-A, Withanone and Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester for Treatment of Aberrant-EGFR Driven Lung Cancers.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 26;11(2):160. doi: 10.3390/biom11020160. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33530424 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Withaferin-A, Withanone, and Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester on DNA Methyltransferases: Potential in Epigenetic Cancer Therapy.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(4):379-391. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666230726105017. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37496252
-
Withanone and caffeic acid phenethyl ester are predicted to interact with main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 and inhibit its activity.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Jul;39(11):3842-3854. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1772108. Epub 2020 Jun 1. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021. PMID: 32431217 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting oncogenic Raf protein-serine/threonine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Sep;135:239-258. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.013. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30118796 Review.
-
Vemurafenib.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014;201:215-25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54490-3_13. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24756795 Review.
Cited by
-
Can Ashwagandha Benefit the Endocrine System?-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 20;24(22):16513. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216513. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Withaferin A: A Pleiotropic Anticancer Agent from the Indian Medicinal Plant Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 22;16(2):160. doi: 10.3390/ph16020160. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

