Prior upregulation of interferon pathways in the nasopharynx impacts viral shedding following live attenuated influenza vaccine challenge in children
- PMID: 35028607
- PMCID: PMC8714852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100465
Prior upregulation of interferon pathways in the nasopharynx impacts viral shedding following live attenuated influenza vaccine challenge in children
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Prior upregulation of interferon pathways in the nasopharynx impacts viral shedding following live attenuated influenza vaccine challenge in children.Cell Rep Med. 2022 Feb 15;3(2):100516. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100516. eCollection 2022 Feb 15. Cell Rep Med. 2022. PMID: 35243419 Free PMC article.
Abstract
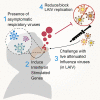
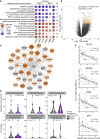
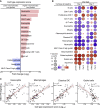
In children lacking influenza-specific adaptive immunity, upper respiratory tract innate immune responses may influence viral replication and disease outcome. We use trivalent live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) as a surrogate challenge model in children aged 24-59 months to identify pre-infection mucosal transcriptomic signatures associated with subsequent viral shedding. Upregulation of interferon signaling pathways prior to LAIV is significantly associated with lower strain-specific viral loads (VLs) at days 2 and 7. Several interferon-stimulated genes are differentially expressed in children with pre-LAIV asymptomatic respiratory viral infections and negatively correlated with LAIV VLs. Upregulation of genes enriched in macrophages, neutrophils, and eosinophils is associated with lower VLs and found more commonly in children with asymptomatic viral infections. Variability in pre-infection mucosal interferon gene expression in children may impact the course of subsequent influenza infections. This variability may be due to frequent respiratory viral infections, demonstrating the potential importance of mucosal virus-virus interactions in children.
Keywords: LAIV; asymptomatic respiratory viral infection; influenza; interferon-stimulated genes; mucosal; transcriptome.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.O.M. reports compensation for consulting services with Cellarity. No other conflicts of interest are reported by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Mallory R.M., Yi T., Ambrose C.S. Shedding of Ann Arbor strain live attenuated influenza vaccine virus in children 6-59 months of age. Vaccine. 2011;29:4322–4327. - PubMed
-
- Lindsey B.B., Jagne Y.J., Armitage E.P., Singanayagam A., Sallah H.J., Drammeh S., Senghore E., Mohammed N.I., Jeffries D., Höschler K., et al. Effect of a Russian-backbone live-attenuated influenza vaccine with an updated pandemic H1N1 strain on shedding and immunogenicity among children in The Gambia: an open-label, observational, phase 4 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019;7:665–676. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 110058/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00026/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A900_1122/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A900_1115/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

