Grand Challenges in global eye health: a global prioritisation process using Delphi method
- PMID: 35028632
- PMCID: PMC8732284
- DOI: 10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00302-0
Grand Challenges in global eye health: a global prioritisation process using Delphi method
Abstract
Background: We undertook a Grand Challenges in Global Eye Health prioritisation exercise to identify the key issues that must be addressed to improve eye health in the context of an ageing population, to eliminate persistent inequities in health-care access, and to mitigate widespread resource limitations.
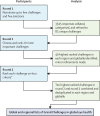
Methods: Drawing on methods used in previous Grand Challenges studies, we used a multi-step recruitment strategy to assemble a diverse panel of individuals from a range of disciplines relevant to global eye health from all regions globally to participate in a three-round, online, Delphi-like, prioritisation process to nominate and rank challenges in global eye health. Through this process, we developed both global and regional priority lists.
Findings: Between Sept 1 and Dec 12, 2019, 470 individuals complete round 1 of the process, of whom 336 completed all three rounds (round 2 between Feb 26 and March 18, 2020, and round 3 between April 2 and April 25, 2020) 156 (46%) of 336 were women, 180 (54%) were men. The proportion of participants who worked in each region ranged from 104 (31%) in sub-Saharan Africa to 21 (6%) in central Europe, eastern Europe, and in central Asia. Of 85 unique challenges identified after round 1, 16 challenges were prioritised at the global level; six focused on detection and treatment of conditions (cataract, refractive error, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, services for children and screening for early detection), two focused on addressing shortages in human resource capacity, five on other health service and policy factors (including strengthening policies, integration, health information systems, and budget allocation), and three on improving access to care and promoting equity.
Interpretation: This list of Grand Challenges serves as a starting point for immediate action by funders to guide investment in research and innovation in eye health. It challenges researchers, clinicians, and policy makers to build collaborations to address specific challenges.
Funding: The Queen Elizabeth Diamond Jubilee Trust, Moorfields Eye Charity, National Institute for Health Research Moorfields Biomedical Research Centre, Wellcome Trust, Sightsavers, The Fred Hollows Foundation, The Seva Foundation, British Council for the Prevention of Blindness, and Christian Blind Mission.
Translations: For the French, Spanish, Chinese, Portuguese, Arabic and Persian translations of the abstract see Supplementary Materials section.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license.
Conflict of interest statement
MJB reports grants (in support of the work of the Lancet Global Health Commission) from The Wellcome Trust, The Queen Elizabeth Diamond Jubilee Trust, Sightsavers, The Fred Hollows Foundation, The British Council for the Prevention of Blindness, Moorfields Eye Charity, The Seva Foundation, and Christian Blind Mission during the conduct of the study. NC reports personal fees from Belkin Vision. DSF reports personal fees from W L Gore, Bausch and Lomb, Life Biosciences, Thea, and iDx outside of the submitted work; and is a member of the Board of Orbis International. TYW reports grants from Allergan, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eden Ophthalmic, Genentech, Iveric Bio, Merck, Novartis, Oxurion (formerly ThromboGenics), Roche, Samsung, Shanghai Henlius, Zhaoke Pharmaceutical, and Aldropika Therapeutics, and is co-founder of start-up companies Plano and EyRiS. PTK reports stockholding for Radiance Therapeutics and Optceutics; personal fees from Aerie, Alcon, AstraZeneca, Bausch + Lomb, Genetech, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi-Aventis outside of the submitted work; being a board member of Moorfields Eye Hospital; and having a patent pending for Biochannel Device. HT reports leadership roles for the International Council of Ophthalmology and the Ophthalmology Foundation (unpaid roles). SKW reports board membership (unpaid) of Christian Blind Mission-USA. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Barriers to eye care for older people in the Philippines.Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022 Mar;3(3):e130. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00025-3. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022. PMID: 36098287 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous