A biomimetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (BELISA) for the analysis of gonadorelin by using molecularly imprinted polymer-coated microplates
- PMID: 35028691
- PMCID: PMC9242967
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-021-03867-7
A biomimetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (BELISA) for the analysis of gonadorelin by using molecularly imprinted polymer-coated microplates
Abstract
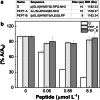
An original biomimetic enzyme-linked immunoassay (BELISA) to target the small peptide hormone gonadorelin is presented. This peptide has been recently listed among the substances banned in sports by the World Antidoping Agency (WADA) since its misuse by male athletes triggers testosterone increase. Hence, in response to this emerging issue in anti-doping controls, we proposed BELISA which involves the growth of a polynorepinephrine (PNE)-based molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) directly on microwells. PNE, a polydopamine (PDA) analog, has recently displayed impressive performances when it was exploited for MIP preparation, giving even better results than PDA. Gonadorelin quantification was accomplished via a colorimetric indirect competitive bioassay involving the competition between biotinylated gonadorelin linked to the signal reporter and the unlabeled analyte. These compete for the same MIP binding sites resulting in an inverse correlation between gonadorelin concentration and the output color signal (λ = 450 nm). A detection limit of 277 pmol L-1 was achieved with very good reproducibility in standard solutions (avCV% = 4.07%) and in urine samples (avCV% = 5.24%). The selectivity of the assay resulted adequate for biological specimens and non-specific control peptides. In addition, the analytical figures of merit were successfully validated by mass spectrometry, the reference anti-doping benchtop platform for the analyte. BELISA was aimed to open real perspectives for PNE-based MIPs as alternatives to antibodies, especially when the target analyte is a poorly or non-immunogenic small molecule, such as gonadorelin. Biomimetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (BELISA).
Keywords: Antibody mimetics; Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Gonadotropin-releasing hormone; Molecularly imprinted polymers; Polydopamine; Polynorepinephrine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Lequin RM. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Chem. 2005. 10.1373/clinchem.2005.051532. - PubMed
-
- Gao L, Yang Q, Wu P, Li F. Recent advances in nanomaterial-enhanced enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Analyst. 2020. 10.1039/d0an00597e. - PubMed
-
- Dos Santos Maciel MO, Soares MF, Costa SF, Bragato JP, de Freitas JH, Venturin GL, Melo LM, Rebech GT, Reed S, de Lima VMF. Development of plasmonicc ELISA for the detection of anti-Leishmania sp. IgG antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 2019. 10.1016/j.jim.2019.112664. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

