Medical Oxygen: A Lifesaving Drug During the COVID-19 Pandemic-Source and Distribution
- PMID: 35029808
- PMCID: PMC8758929
- DOI: 10.1007/s12098-021-03978-0
Medical Oxygen: A Lifesaving Drug During the COVID-19 Pandemic-Source and Distribution
Abstract
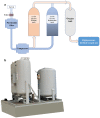
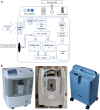
Oxygen is an essential lifesaving medicine used for several indications at all levels of health care. The COVID-19 pandemic and its recent second wave have resulted in a surge in demand for necessary resources, including trained staff, hospital beds, and medical supplies like oxygen. Limited availability of these resources resulted in added risk of adverse outcomes. Also, the widespread unregulated use of oxygen by the general public in household settings poses safety concerns. This review focuses on sources of medical oxygen like cryogenic oxygen plants, pressure swing adsorption, oxygen concentrators, and oxygen cylinders. Their specifications, storage, distribution within healthcare settings, regulation, and safety concerns have been considered. Resources needed for calculating oxygen demand, surge planning, identifying the suitable source, and distribution systems for different settings have been detailed. This review aims to help the hospital administrators, biomedical engineers, and clinicians plan and rationalize oxygen usage in low- and middle-income countries during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cryogenic distillation; Medical oxygen; Oxygen concentrators; Oxygen cylinders; Pressure swing adsorption.
© 2021. Dr. K C Chaudhuri Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Centre undertakes multiple initiatives to enhance oxygen availability, distribution and storage infrastructure. PIB, Government of India. 2021. Available at: https://pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=1717459. Accessed on 11th May 2021.
-
- COVID-19 Oxygen Needs Tracker. Path. 2021. Available at: https://www.path.org/programs/market-dynamics/covid-19-oxygen-needs-trac.... Accessed on 11th May 2021.
-
- Kaushik M. How many more lives could be lost in India’s oxygen crisis? Scroll.in. 2021. Available at: https://scroll.in/article/994252/how-many-more-lives-could-be-lost-in-in.... Accessed on 11th May 2021.
-
- WHO technical specifications for oxygen concentrators. World Health Organization. 2015. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241509886. Accessed on 14th May 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

