Comparison of the effects of remifentanil and dexmedetomidine on surgeon satisfaction with surgical field visualization and intraoperative bleeding during rhinoplasty
- PMID: 35031005
- PMCID: PMC8759207
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-021-01546-9
Comparison of the effects of remifentanil and dexmedetomidine on surgeon satisfaction with surgical field visualization and intraoperative bleeding during rhinoplasty
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to compare the effect of dexmedetomidine with remifentanil on hemodynamic stability, surgical field quality, and surgeon satisfaction during rhinoplasty.
Methods and materials: In this double-blind randomized controlled-trial, 60 participants scheduled for rhinoplasty at the Mother and Child Hospital, Shiraz, Iran, was randomely divided into the dexmedetomidine group (IV infusion of 1 μg/kg dexmedetomidine over 20 min before induction of anesthesia then 0.6 μg/kg/hr. dexmedetomidine from the time of induction until the end of the operation) or in the the remifentanil group (an infusion rate of 0.25 μg/kg/min from the time of anesthesia induction until the end of the operation). Bleeding volume, surgeon satisfaction, postoperative pain (visual analog scale (VAS)), Level of sedation (Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS)), Patient satisfaction, Vital signs & recovery, and the Aldrete Score (used to discharge the patients from recovery) were measured for all participants.
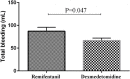
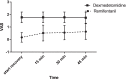
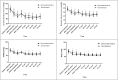
Results: The patients in the dexmedetomidine group had less bleeding (p = 0.047) and shorter time to return of respiration, extubation, and the postoperative recovery time (p < 0.001). The surgeon satisfaction was higher in the dexmedetomidine group (p < 0.001). Patient satisfaction was significantly different between the two groups (p < 0.001). VAS scores, intaking paracetamol, and RASS score were significantly lower in the remifentanil group (p < 0.001). SBP, DBP, MAP, and heart rate were lower in dexmedetomidine group.
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine was associated with relatively stable hemodynamics, leading to decreased intraoperative bleeding, recovery time, and greater surgeon satisfaction and the level of consciousness in the recovery ward. However, painlessness and patient satisfaction were greater with the use of remifentanil.
Trial registration: IRCT20141009019470N112 .
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; Remifentanil; Rhinoplasty.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study between remifentanil (or fentanyl) and dexmedetomidine for the analgesia of rhinoplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Apr 19;103(16):e37020. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037020. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38640315 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of dexmedetomidine, remifentanil and metoral in reducing patient bleeding during rhinoplasty surgery.Int Tinnitus J. 2024 Mar 21;27(2):154-159. doi: 10.5935/0946-5448.20230024. Int Tinnitus J. 2024. PMID: 38507629 Clinical Trial.
-
Application of dexmedetomidine-remifentanil in high-intensity ultrasound ablation of uterine fibroids: a randomised study.BJOG. 2017 Aug;124 Suppl 3:23-29. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.14740. BJOG. 2017. PMID: 28856857 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Effect of Dexmedetomidine and Remifentanil on Controlled Hypotension During Rhinoplasty: A Clinical Trial Study.Int Tinnitus J. 2021 Jan 25;24(2):60-64. doi: 10.5935/0946-5448.20200013. Int Tinnitus J. 2021. PMID: 33496413 Clinical Trial.
-
Dexmedetomidine versus remifentanil in nasal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 May 30;24(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02563-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38816731 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Randomized single-blinded study comparing sedation effectiveness and hemodynamic stability of remifentanil vs dexmedetomidine infusion for electrophysiology procedures in patients of National Heart Institute cathlab.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2024 Nov;67(8):1735-1743. doi: 10.1007/s10840-024-01884-x. Epub 2024 Aug 7. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2024. PMID: 39110272 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative study between remifentanil (or fentanyl) and dexmedetomidine for the analgesia of rhinoplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Apr 19;103(16):e37020. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037020. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38640315 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine regulates the anti-oxidation and autophagy of adipose-derived stromal cells under H2O2-induced oxidative stress through Nrf2/p62 pathway and improves the retention rate of autologous fat transplantation.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 25;15:1453938. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1453938. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39654626 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Relationship between Baseline Autonomic Tone and Haemodynamic Effects of Dexmedetomidine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Feb 25;16(3):354. doi: 10.3390/ph16030354. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986456 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Effect of Pressure-Controlled Versus Volume-Controlled Ventilation Modes on Intraoperative Bleeding in Rhinoplasty: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Anesth Pain Med. 2024 Oct 29;14(5):e151582. doi: 10.5812/aapm-151582. eCollection 2024 Oct. Anesth Pain Med. 2024. PMID: 40078656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- SJdA d V, do Nascimento-Júnior EM, de Aguiar Menezes MV, MLT M, de Souza Dantas R, PRSJ M-F, et al. Preoperative tranexamic acid for treatment of bleeding, edema, and ecchymosis in patients undergoing rhinoplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;144(9):816–823. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2018.1381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

