Effect of six-week traditional resistance and functional training on functional performance in female netball players
- PMID: 35033152
- PMCID: PMC8760794
- DOI: 10.1186/s13102-022-00402-8
Effect of six-week traditional resistance and functional training on functional performance in female netball players
Abstract
Background: Improving the quality of functional movements in athletes generally requires additional training targeting specific functional deficiencies. However, well-rounded, traditional strength and conditioning program should also improve player's movement quality. Therefore, the primary aim of this study was to compare the effect of two different six-week interventions on the functional score of female netball players.
Methods: In a randomized controlled study, players were divided into control and intervention group. Both groups completed identical six-week strength and conditioning program, with the intervention group also completing additional corrective exercises three sessions per week during the same period.
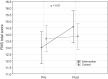
Results: The FMS® score was significantly higher in the intervention group after 6-week program (f = 9.85, p = 0.004). However, the differences in total score may be attributed mainly to differences between groups in active straight leg raise (p = 0.004) and trunk stability push-up test (p = 0.02), as other individual tests demonstrated similar time and group effect.
Conclusion: These results indicate that although FMS® based intervention may improve overall functional movement score, the athletes in both groups have demonstrated similar improvements in most of the individual tests. Hence, a well-rounded strength and conditioning program incorporating athlete-specific exercises based on limitations identified in the functional movement screen, may result in a balanced training strategy and reduce the need for supplementary functional training sessions.
Keywords: FMS®; Functional training; Sport performance; Strength and conditioning.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of functional movement screen training in high-school baseball players: A randomized controlled clinical trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 9;100(14):e25423. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025423. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33832142 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of 8-Week Functional vs. Traditional Training on Athletic Performance and Functional Movement on Prepubertal Tennis Players.J Strength Cond Res. 2019 Mar;33(3):651-661. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002956. J Strength Cond Res. 2019. PMID: 30431536
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
Short-term Periodization Models: Effects on Strength and Speed-strength Performance.Sports Med. 2015 Oct;45(10):1373-86. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0355-2. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26133514 Review.
-
Biomechanical factors affecting performance in netball. Implications for improving performance and injury reduction.Sports Med. 1990 Aug;10(2):88-102. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199010020-00003. Sports Med. 1990. PMID: 2204101 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative function of proprioceptive system in the acute effects of whole body vibration on the movement performance in young adults.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 Apr 9;6:1357199. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1357199. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 38654753 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of functional training on sprinting, jumping, and functional movement in athletes: A systematic review.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 30;13:1045870. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1045870. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36531163 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of six-week flywheel and traditional resistance training on deceleration and dynamic balance in elite badminton players.Front Physiol. 2025 Feb 25;16:1491661. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1491661. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40070459 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a 12-Week Functional Training Program on the Strength and Power of Chinese Adolescent Tennis Players.Children (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;10(4):635. doi: 10.3390/children10040635. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37189884 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Injury Prevention Using Functional Movement Screen Training in High-School Baseball Players: Secondary Outcomes of a Randomized Controlled Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;10(12):2409. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10122409. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553933 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous