Comparison of surgical outcomes and prognosis between wedge resection and simple Segmentectomy for GGO diameter between 2 cm and 3 cm in non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter and propensity score matching analysis
- PMID: 35034626
- PMCID: PMC8761309
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-09129-0
Comparison of surgical outcomes and prognosis between wedge resection and simple Segmentectomy for GGO diameter between 2 cm and 3 cm in non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter and propensity score matching analysis
Abstract
Background: As segmentectomy had become commonly used for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) treatment, which had the advantages of radical operation, however, it remains controversial owing to procedural complexity and risk of increased complications compared with wedge resection. We evaluated operative and postoperative outcomes of simple segmentectomy compared to wedge resection in ground-glass opacity (GGO) diameter between 2 cm and 3 cm NSCLC.
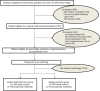
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 1600 clinical GGO diameter between 2 cm and 3 cm NSCLC patients who received simple segmentectomy and wedge resection between Jan 2011 and Jan 2015. Participants were matched 1:1 on their propensity score for two groups. Clinic-pathologic, operative, and postoperative results of two groups were compared.
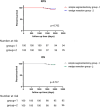
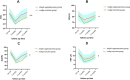
Results: After using propensity score methods to create a matched cohort of participants with simple segmentectomy group similar to that wedge resection, there were no significant differences detected in tumor size, margin distance, histology, age, sex, preoperative comorbidities and preoperative pulmonary function. Overall complications in simple segmentectomy group were more than wedge resection group (21% vs 3%, p = 0.03). Median operative time (110.6 vs. 71.2 min; p = 0.01) and prolonged air leakage (12% vs. 3%; p = 0.02) was significantly longer in the simple segmentectomy group. There was no difference in recurrence free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) of 5-years between simple segmentectomy group and wedge resection group. Postoperative pulmonary function in simple segmentectomy group recovered more slowly than wedge resection group.
Conclusion: Wedge resection may have comparable efficacy as simple segmentectomy for GGO diameter between 2 cm and 3 cm NSCLC, but lead to less complications, less surgical procedure and faster recovery of pulmonary function.
Keywords: Ground-glass opacity; NSCLC; Propensity score matching; Segmentectomy; Wedge resection.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intentional wedge resection versus segmentectomy for ≤2 cm ground-glass-opacity-dominant non-small cell lung cancer: a real-world study using inverse probability of treatment weighting.Int J Surg. 2024 Jul 1;110(7):4231-4239. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001361. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38518080 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Procedure Selection for Stage I Lung Cancer: Complex Segmentectomy versus Wedge Resection.Clin Lung Cancer. 2021 Mar;22(2):e224-e233. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.10.021. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Clin Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33334701
-
Wedge resection versus segmentectomy in patients with stage I non-small-cell lung cancer unfit for lobectomy.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019 Dec 27;49(12):1134-1142. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyz122. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31602468
-
Are segmentectomy and lobectomy comparable in terms of curative intent for early stage non-small cell lung cancer?Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Jul;68(7):703-706. doi: 10.1007/s11748-019-01219-y. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 31691886 Review.
-
Oncological Outcomes of Lobar Resection, Segmentectomy, and Wedge Resection for T1a Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Autumn;32(3):582-590. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2019.08.004. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 31401180
Cited by
-
Risk factors for postoperative cerebral infarction in patients after lung resection: a single-center case-control study.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Feb 28;15(2):376-385. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1019. Epub 2023 Jan 16. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 36910048 Free PMC article.
-
Uniportal VATS for Diagnosis and Staging in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;13(5):826. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13050826. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36899970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thoracoscopic segmentectomy for trans-fissure ground-glass opacity.Interdiscip Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2024 May 2;38(5):ivae090. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivae090. Interdiscip Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38724246 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of segmentectomy vs. wedge resection for the treatment of patients with operable non‑small cell lung cancer: A meta‑analysis and systematic review.Oncol Lett. 2024 May 24;28(1):336. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14469. eCollection 2024 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38846430 Free PMC article.
-
Faster, safer, better recovery: a modified robotic-assisted segmentectomy versus conventional approaches in early stage lung cancer.J Robot Surg. 2025 Aug 9;19(1):465. doi: 10.1007/s11701-025-02640-7. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 40781576
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

