Personalized nursing improves physical condition and life quality of patients undergoing interventional therapy for liver cancer
- PMID: 35035768
- PMCID: PMC8748081
Personalized nursing improves physical condition and life quality of patients undergoing interventional therapy for liver cancer
Abstract
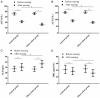
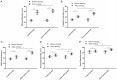
Interventional therapy, which can prolong the survival of patients with liver cancer (LC), is an important means to treat the disease. During interventional therapy for LC, it is essential to make a targeted and detailed nursing plan to ameliorate the prognosis. The purpose of this study was to determine the application significance of personalized nursing in patients undergoing interventional therapy for LC. We retrospectively analyzed 136 patients with LC undergoing interventional therapy. Among them, 70 cases receiving personalized nursing were assigned to the observation group (OG), and the remaining 66 cases receiving routine nursing were the control group (CG). After nursing, sleep time of patients in the OG was significantly longer than that in CG. In addition, time to ambulation and hospital stay were shorter in the OG than in the CG. Furthermore, the OG exhibited significantly lower scores of visual analogue scale (VAS) and self-rating anxiety scale (SAS), as well as significantly reduced incidence of adverse reactions than the CG. Compared with the CG, the levels of serum alanine aminotransferase (AST), aspartate aminotransferase (ALT), and total bilirubin (TBIL) were significantly lower in the OG after nursing, while the level of albumin (ALB) was significantly increased. Moreover, patients in the OG showed significantly higher nursing satisfaction and quality of life scores than those in the CG. Therefore, personalized nursing has good prospects for usein interventional therapy for LC.
Keywords: Liver cancer; interventional therapy; personalized nursing; quality of life.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on inflammation and liver function after laparoscopic radical resection of primary liver cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Nov 15;14(11):8156-8165. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36505328 Free PMC article.
-
Specific nursing improves postoperative urine control function and the self-efficacy of patients undergoing radical prostatectomies.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Mar 15;14(3):1695-1704. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35422910 Free PMC article.
-
High-quality nursing can reduce the incidence of adverse events in esophageal cancer patients after operation in the intensive care unit and improve postoperative rehabilitation.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Oct 15;13(10):11851-11859. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34786114 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of total enteral nutrition via nasal feeding and percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy in patients with dysphagia following a cerebral infarction.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Jun 15;13(6):6352-6361. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34306374 Free PMC article.
-
The application effects of personalized nursing on the perioperative period of hepatobiliary surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Sep;10(9):9583-9593. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1923. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34628884
Cited by
-
Effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on inflammation and liver function after laparoscopic radical resection of primary liver cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Nov 15;14(11):8156-8165. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36505328 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized nursing as the missing link of providing care: A systematic review.BMC Nurs. 2025 Mar 3;24(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-02855-x. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40033310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao W, Qiu L, Liu H, Xu Y, Zhan M, Zhang W, Xin Y, He X, Yang X, Bai J, Xiao J, Guan Y, Li Q, Chang L, Yi X, Li Y, Chen X, Lu L. Circulating tumor DNA as a potential prognostic and predictive biomarker during interventional therapy of unresectable primary liver cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020;11:1065–1077. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Si MB, Yan PJ, Hao XY, Du ZY, Tian HW, Yang J, Han CW, Yang KH, Guo TK. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation versus minimally invasive liver surgery for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2019;33:2419–2429. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
