Whole-blood cytokine secretion assay as a high-throughput alternative for assessing the cell-mediated immunity profile after two doses of an adjuvanted SARS-CoV-2 recombinant protein vaccine candidate
- PMID: 35035955
- PMCID: PMC8752373
- DOI: 10.1002/cti2.1360
Whole-blood cytokine secretion assay as a high-throughput alternative for assessing the cell-mediated immunity profile after two doses of an adjuvanted SARS-CoV-2 recombinant protein vaccine candidate
Abstract
Objectives: We previously described the Phase I-II evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 recombinant protein candidate vaccine, CoV2-PreS-dTM, with AF03- or AS03-adjuvant systems (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04537208). Here, we further characterise the cellular immunogenicity profile of this vaccine candidate using a whole-blood secretion assay in parallel to intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) of cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).
Methods: A randomly allocated subset of 90 healthy, SARS-CoV-2-seronegative adults aged ≥ 18 years who had received (random allocation) one or two separate injections (on study day [D]1 and D22) of saline placebo or CoV2-PreS-dTM formulated with AS03 or AF03 were included. Cytokine secretion was assessed using a TruCulture® whole-blood stimulation system in combination with multiplex bead array, and intracellular cytokine profiles were evaluated on thawed PBMCs following ex vivo stimulation with recombinant S protein at pre-vaccination (D1), post-dose 1 (D22) and post-dose 2 (D36).
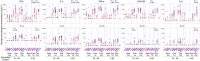
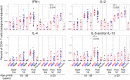
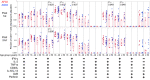
Results: Both methods detected similar vaccine-induced responses after the first and second doses. We observed a Th1 bias (Th1/Th2 ratio > 1.0) for most treatment groups when analysed in whole blood, mainly characterised by increased IFN-γ, IL-2 and TNF-α secretion. Among participants aged ≥ 50 years, the Th1/Th2 ratio was higher for those who received vaccine candidate with AS03 versus AF03 adjuvant. ICS revealed that this higher Th1/Th2 ratio resulted from higher levels of IFN-γ expression and that the vaccine induced polyfunctional CD4+ T cells.
Conclusions: The whole-blood cytokine secretion assay is a high-throughput alternative for assessing the quantity and character of vaccine-induced cellular responses.
Keywords: AF03; AS03; CoV2‐PreS‐dTM; SARS‐CoV‐2 recombinant protein candidate vaccine; adjuvant; cell‐mediated immunity; intracellular cytokine staining; multiplex bead array; whole‐blood cytokine secretion assay.
© 2022 Sanofi Pasteur. Clinical & Translational Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
SdR, KC, YH, MJM and DM are employees of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. The Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center received funding from Sanofi Pasteur through a contract to perform the ICS analysis. MIB, BF, SG, DL, GdB and AP are Sanofi Pasteur employees and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. CG and RVdM are employed by, and hold restricted shares in, the GlaxoSmithKline group of companies. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Regulatory Affairs Professionals Society (RAPS) . COVID‐19 vaccine tracker. 2021. Available at https://www.raps.org/news‐and‐articles/news‐articles/2020/3/covid‐19‐vac.... Accessed on 27 April 2021.
-
- Gavi The Vaccine Alliance . Four reasons why we need multiple vaccines for Covid‐19. Available at https://www.gavi.org/vaccineswork/four‐reasons‐why‐we‐need‐multiple‐vacc.... Accessed 06 July 2021.
-
- European Medicines Agency . Committee on human medicinal products: Guideline on clinical evaluation of vaccines (draft). 2018. Available at https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific‐guideline/draft‐guidel.... Accessed 19 July 2021.
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines on clinical evaluation of vaccines: regulatory expectations: Revision of WHO TRS 924, Annex 1. 2016. Available at https://www.who.int/biologicals/expert_committee/Clinical_changes_IK_fin.... Accessed 19 July 2021.
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
