Effects and Mechanism of Oxymatrine Combined with Compound Yinchen Granules on the Apoptosis of Hepatocytes through the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim Pathway
- PMID: 35036441
- PMCID: PMC8758272
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8644356
Effects and Mechanism of Oxymatrine Combined with Compound Yinchen Granules on the Apoptosis of Hepatocytes through the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim Pathway
Abstract
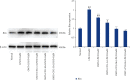
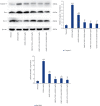
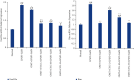
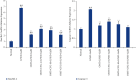
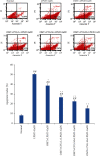
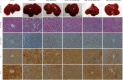
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects and mechanism of oxymatrine (OMT) combined with compound yinchen granules (CYG) on the apoptosis of hepatocytes through the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim pathway in rats with acute liver failure. The rat model of acute liver failure was established using lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine (LPS/D-GalN). The expression of proteins in rat liver tissues was detected by western blot analysis. The mRNA expression of FoxO3a, Bim, Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 in rat liver tissues was detected by RT-qPCR. The apoptosis rate of rat hepatocytes was determined by flow cytometry. Western blots showed that when compared with the normal group, the expression of p-Akt and p-FoxO3a in the model group was decreased (P < 0.05), while the expression of Bim was increased (P < 0.01). Compared with the model group, the expression of p-Akt and p-FoxO3a in the OMT group and the OMT combined with CYG groups was increased (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), while the expression of Bim was decreased (P < 0.05). The Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 protein expression in the model group were significantly higher than those in the normal group (P < 0.01). The Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and the expression of caspase-3 protein in the OMT group and the OMT combined with CYG groups were significantly lower than those in the model group (P < 0.01). The results of RT-qPCR were consistent with those of western blot. The results of flow cytometry showed that the apoptosis rate of hepatocytes in the OMT group and the OMT combined with CYG groups was significantly lower than that in the model group (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). We concluded that LPS/D-GalN can induce apoptosis of hepatocytes in rats with acute liver failure through the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim pathway. OMT combined with CYG inhibits apoptosis of hepatocytes in rats with acute liver failure via the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim pathway.
Copyright © 2022 Xian Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

