Formulation and Evaluation of Luteolin-Loaded Nanovesicles: In Vitro Physicochemical Characterization and Viability Assessment
- PMID: 35036768
- PMCID: PMC8757359
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05628
Formulation and Evaluation of Luteolin-Loaded Nanovesicles: In Vitro Physicochemical Characterization and Viability Assessment
Abstract
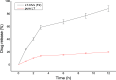
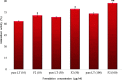
Luteolin (LT) is a natural polyphenol water-insoluble compound. LT-loaded nanovesicles (NVs) were prepared by using the solvent evaporation method. LT-NVs were prepared using cholesterol, phosphatidylcholine, span 60, and labrasol in a different composition. The prepared LT-NVs were evaluated for encapsulation efficiency, in vitro drug release, and permeation study. The optimized LT-NVs were further evaluated for antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity using the lung cancer cell line. LT-NVs showed nanometric size (less than 300 nm), an optimum polydispersibility index (less than 0.5), and a negative zeta potential value. The formulations also showed significant variability in the encapsulation efficiency (69.44 ± 0.52 to 83.75 ± 0.35%) depending upon the formulation composition. The in vitro and permeation study results revealed enhanced drug release as well as permeation profile. The formulation LT-NVs (F2) showed the maximum drug release of 88.28 ± 1.13%, while pure LT showed only 20.1 ± 1.21% in 12 h. The release data revealed significant variation (p < 0.001) in the release pattern. The permeation results also depicted significant (p < 0.001) enhancement in the permeation across the membrane. The enhanced permeation from LT-NVs was achieved due to the enhanced solubility of LT in the presence of the surfactant. The antioxidant activity results proved that LT-NVs showed greater activity compared to pure LT. The cytotoxicity study showed lesser IC50 value from LT-NVs than the pure LT. Thus, it can be concluded that LT-NVs are a natural alternative to the synthetic drug in the treatment of lung cancer.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Formulation, Optimization and Evaluation of Luteolin-Loaded Topical Nanoparticulate Delivery System for the Skin Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 20;13(11):1749. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111749. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834164 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation of Chitosan-Coated Apigenin Bilosomes: In Vitro Characterization, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity Assessment.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 25;14(5):921. doi: 10.3390/polym14050921. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267744 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of luteolin loaded pegylated bilosome: optimization, in vitro characterization, and cytotoxicity study.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):2562-2573. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2008055. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34866534 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation of Piperine-Chitosan-Coated Liposomes: Characterization and In Vitro Cytotoxic Evaluation.Molecules. 2021 May 29;26(11):3281. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113281. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34072306 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-nanovesicles interplay for theranostics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024 Feb;205:115176. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.115176. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024. PMID: 38199256 Review.
Cited by
-
Nano-Drug Delivery Systems Entrapping Natural Bioactive Compounds for Cancer: Recent Progress and Future Challenges.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 29;12:867655. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.867655. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35425710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The combination of polyphenols and phospholipids as an efficient platform for delivery of natural products.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 13;13(1):2501. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29237-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36781871 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin: exploring its therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms in pulmonary diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 12;16:1535555. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1535555. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40012626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of plant metabolites hinders starch digestion and glucose absorption while facilitating insulin sensitivity to diabetes.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 5;15:1362150. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1362150. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38903985 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the Therapeutic Effect and Bioavailability of Irradiated Silver Nanoparticle-Capped Chitosan-Coated Rosuvastatin Calcium Nanovesicles for the Treatment of Liver Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jan 7;17(1):72. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010072. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 39861720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiménez-López J.; El-Hammadi M. M.; Ortiz R.; Cayero-Otero M. D.; Cabeza L.; Perazzoli G.; Martin-Banderas L.; Baeyens J. M.; Prados J.; Melguizo C. A novel nanoformulation of PLGA with high non-ionic surfactant content improves in vitro and in vivo PTX activity against lung cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 141, 451–465. 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.01.013. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

