Can telerehabilitation services combined with caregiver-mediated exercises improve early supported discharge services poststroke? A study protocol for a multicentre, observer-blinded, randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 35039010
- PMCID: PMC8762867
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-021-02533-w
Can telerehabilitation services combined with caregiver-mediated exercises improve early supported discharge services poststroke? A study protocol for a multicentre, observer-blinded, randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Recovery of walking ability is an important goal for patients poststroke, and a basic level of mobility is critical for an early discharge home. Caregiver-mediated exercises could be a resource-efficient strategy to augment exercise therapy and improve mobility in the first months poststroke. A combination of telerehabilitation and face-to-face support, blended care, may empower patient-caregiver dyads and smoothen the transition from professional support to self-management. The Armed4Stroke study aims to investigate the effects of a caregiver-mediated exercise program using a blended care approach in addition to usual care, on recovery of mobility in the first 6 months poststroke.
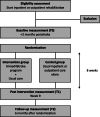
Methods: A multicentre, observer-blinded randomized clinical trial in which 74 patient-caregiver dyads will be enrolled in the first 3 months poststroke. Dyads are randomly allocated to a caregiver-mediated exercises intervention or to a control group. The primary endpoint is the self-reported mobility domain of the Stroke Impact Scale. Secondary endpoints include care transition preparedness and psychological functioning of dyads, length of inpatient stay, gait-related measures and extended ADL of patients, and caregiver burden. Outcomes are assessed at enrolment, end of treatment and 6 months follow-up.
Results: During 8 weeks, caregivers are trained to become an exercise coach using a blended care approach. Dyads will receive a tailor-made, progressive training program containing task-specific exercises focusing on gait, balance, physical activity and outdoor activities. Dyads are asked to perform the training program a minimum of 5 times a week for 30 min per session, supported by a web-based telerehabilitation system with instruction videos and a messaging environment to communicate with their physiotherapist.
Conclusions: We hypothesize that the Armed4Stroke program will increase self-reported mobility and independence in ADL, facilitating an early discharge poststroke. In addition, we hypothesize that active involvement of caregivers and providing support using blended care, will improve the care transition when professional support tapers off. Therefore, the Armed4Stroke program may complement early supported discharge services.
Trial registration: Netherlands Trial Register, NL7422 . Registered 11 December 2018.
Keywords: Caregivers; Clinical trial protocol; Exercise; Stroke; Telerehabilitation; Walking.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
-
- James SL, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Warlow C, van Gijn J, Dennis M, Wardlaw J, Bamford J, Hankey G, et al. Stroke: practical management. 3. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; 2008.
-
- Miller EL, Murray L, Richards L, Zorowitz RD, Bakas T, Clark P, et al. Comprehensive overview of nursing and interdisciplinary rehabilitation care of the stroke patient: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Stroke. 2010;41(10):2402–2448. doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e3181e7512b. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical