Neuropsychopharmacological profiling of scoparone in mice
- PMID: 35039558
- PMCID: PMC8764054
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-04741-3
Neuropsychopharmacological profiling of scoparone in mice
Abstract
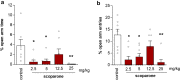
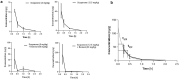
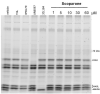
Scoparone (6,7-dimethoxycoumarin) is a simple coumarin from botanical drugs of Artemisia species used in Traditional Chinese Medicine and Génépi liquor. However, its bioavailability to the brain and potential central effects remain unexplored. We profiled the neuropharmacological effects of scoparone upon acute and subchronic intraperitoneal administration (2.5-25 mg/kg) in Swiss mice and determined its brain concentrations and its effects on the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and related lipids using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Scoparone showed no effect in the forced swimming test (FST) but, administered acutely, led to a bell-shaped anxiogenic-like behavior in the elevated plus-maze test and bell-shaped procognitive effects in the passive avoidance test when given subchronically and acutely. Scoparone rapidly but moderately accumulated in the brain (Cmax < 15 min) with an apparent first-order elimination (95% eliminated at 1 h). Acute scoparone administration (5 mg/kg) significantly increased brain arachidonic acid, prostaglandins, and N-acylethanolamines (NAEs) in the FST. Conversely, subchronic scoparone treatment (2.5 mg/kg) decreased NAEs and increased 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Scoparone differentially impacted ECS lipid remodeling in the brain independent of serine hydrolase modulation. Overall, the unexpectedly potent central effects of scoparone observed in mice could have toxicopharmacological implications for humans.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Detsi A, Kontogiorgis C, Hadjipavlou-Litina D. Coumarin derivatives: An updated patent review (2015–2016) Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017;27:1201–1226. - PubMed
-
- Skalicka-Woźniak K, Orhan IE, Cordell GA, Nabavi SM, Budzyńska B. Implication of coumarins towards central nervous system disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2016;103:188–203. - PubMed
-
- Liu, B. et al. Scoparone Alleviates Inflammation, Apoptosis and Fibrosis of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice. International Immunopharmacology vol. 75 105797 (Elsevier B.V., 2019). - PubMed
-
- Goryaev, M. I., Sharipova, F. S., El’chibekova, L. A. & Averina, V. Y. Essential oil of Artemisia scoparia. Chem. Nat. Compd.17, 400–403 (1981).
-
- Boggia L, et al. Artemisia umbelliformis Lam. and Génépi Liqueur: Volatile profile as diagnostic marker for geographic origin and to predict liqueur safety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017;65:2849–2856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

