Therapeutic potential of highly functional codon-optimized microutrophin for muscle-specific expression
- PMID: 35039573
- PMCID: PMC8764061
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-04892-x
Therapeutic potential of highly functional codon-optimized microutrophin for muscle-specific expression
Abstract
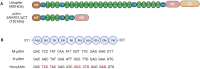
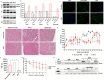
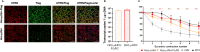
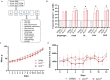
High expectations have been set on gene therapy with an AAV-delivered shortened version of dystrophin (µDys) for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), with several drug candidates currently undergoing clinical trials. Safety concerns with this therapeutic approach include the immune response to introduced dystrophin antigens observed in some DMD patients. Recent reports highlighted microutrophin (µUtrn) as a less immunogenic functional dystrophin substitute for gene therapy. In the current study, we created a human codon-optimized µUtrn which was subjected to side-by-side characterization with previously reported mouse and human µUtrn sequences after rAAV9 intramuscular injections in mdx mice. Long-term studies with systemic delivery of rAAV9-µUtrn demonstrated robust transgene expression in muscles, with localization to the sarcolemma, functional improvement of muscle performance, decreased creatine kinase levels, and lower immunogenicity as compared to µDys. An extensive toxicity study in wild-type rats did not reveal adverse changes associated with high-dose rAAV9 administration and human codon-optimized µUtrn overexpression. Furthermore, we verified that muscle-specific promoters MHCK7 and SPc5-12 drive a sufficient level of rAAV9-µUtrn expression to ameliorate the dystrophic phenotype in mdx mice. Our results provide ground for taking human codon-optimized µUtrn combined with muscle-specific promoters into clinical development as safe and efficient gene therapy for DMD.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mendell JR, Lloyd-Puryear M. Report of MDA muscle disease symposium on newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 2013;48:21–26. - PubMed
-
- Gramolini AO, Jasmin BJ. Molecular mechanisms and putative signalling events controlling utrophin expression in mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD. 1998;8:351–361. - PubMed
-
- Clerk A, Morris GE, Dubowitz V, Davies KE, Sewry CA. Dystrophin-related protein, utrophin, in normal and dystrophic human fetal skeletal muscle. Histochem. J. 1993;25:554–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

