Mechanically robust supramolecular polymer co-assemblies
- PMID: 35042887
- PMCID: PMC8766479
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28017-0
Mechanically robust supramolecular polymer co-assemblies
Abstract
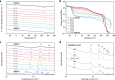
Supramolecular polymers are formed through non-covalent, directional interactions between monomeric building blocks. The assembly of these materials is reversible, which enables functions such as healing, repair, or recycling. However, supramolecular polymers generally fail to match the mechanical properties of conventional commodity plastics. Here we demonstrate how strong, stiff, tough, and healable materials can be accessed through the combination of two metallosupramolecular polymers with complementary mechanical properties that feature the same metal-ligand complex as binding motif. Co-assembly yields materials with micro-phase separated hard and soft domains and the mechanical properties can be tailored by simply varying the ratio of the two constituents. On account of toughening and physical cross-linking effects, this approach affords materials that display higher strength, toughness, or failure strain than either metallosupramolecular polymer alone. The possibility to combine supramolecular building blocks in any ratio further permits access to compositionally graded objects with a spatially modulated mechanical behavior.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Brunsveld L, Folmer BJB, Meijer EW, Sijbesma RP. Supramolecular polymers. Chem. Rev. 2001;101:4071–4098. - PubMed
-
- Yang L, Tan X, Wang Z, Zhang X. Supramolecular polymers: historical development, preparation, characterization, and functions. Chem. Rev. 2015;115:7196–7239. - PubMed
-
- Schubert, U. S., Newkome, G. R. & Winter, A. Supramolecular Polymers and Assemblies: From Synthesis to Properties and Applications (Wiley-VCH, 2021).
-
- Sijbesma RP, et al. Reversible polymers formed from self-complementary monomers using quadruple hydrogen bonding. Science. 1997;278:1601–1604. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

