Novel pathway for the sonochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles with near-spherical shape and high stability in aqueous media
- PMID: 35042912
- PMCID: PMC8766478
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-04921-9
Novel pathway for the sonochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles with near-spherical shape and high stability in aqueous media
Abstract
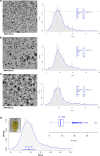
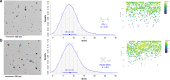
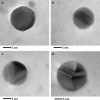
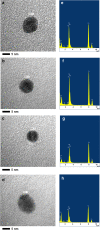
The present study shows the development of a novel sonochemical synthesis pathway of sub-15 nm silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with quasi-spherical shape and high stability in aqueous suspension. Different analytical techniques such as on-line UV-Vis spectroscopy, Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) were complementarily used to characterize the evolution of the properties of AgNPs synthesized with this new route. Furthermore, different centrifugation conditions were studied to establish a practical, simple and straightforward purification method. Particle size was determined by TEM employing two different deposition methods, showing that purified AgNPs have a size of 8.1 nm ± 2.4 nm with a narrow dispersion of the size distribution (95% coverage interval from 3.4 to 13 nm). Critical information of the shape and crystalline structure of these sub-15 nm AgNPs, provided by shape descriptors (circularity and roundness) using TEM and high resolution (HR)-TEM measurements, confirmed the generation of AgNPs with quasi-spherical shapes with certain twin-fault particles promoted by the high energy of the ultrasonic treatment. Elemental analysis by TEM-EDS confirmed the high purity of the sub-15 nm AgNPs, consisting solely of Ag. At the optical level, these AgNPs showed a bandgap energy of (2.795 ± 0.002) eV. Finally, the evaluation of the effects of ultraviolet radiation (UVC: 254 nm and UVA: 365 nm) and storage temperature on the spectral stability revealed high stability of the optical properties and subsequently dimensional properties of sub-15 nm AgNPs in the short-term (600 min) and long-term (24 weeks).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Aqueous Extracts of Allium sativum, Zingiber officinale, and Capsicum frutescens.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jul;13(Suppl 2):S201-S208. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_430_16. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28808381 Free PMC article.
-
Ecofriendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Euphrasia officinalis leaf extract and its biomedical applications.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;46(6):1163-1170. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1362417. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 28784039
-
Caulerpa racemosa: a marine green alga for eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its catalytic degradation of methylene blue.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2016 Sep;39(9):1401-8. doi: 10.1007/s00449-016-1616-7. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2016. PMID: 27129459
-
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Effect of Dextran Molecular Weight Used as Stabilizing-Reducing Agent.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015 Dec;15(12):9849-55. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10334. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26682423
-
Marine plant mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mangrove Rhizophora stylosa: Effect of variable process and their antibacterial activity.F1000Res. 2022 May 16;10:768. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.54661.2. eCollection 2021. F1000Res. 2022. PMID: 37359252 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synthesis characterization and application of butyl acrylate mediated eco-friendly silver nanoparticles using ultrasonic radiation.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 21;10(7):e28309. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28309. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38560218 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the Growth of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Microorganisms in Aesthetic Orthodontic Brackets through the In Situ Synthesis of Ag, TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 Nanoparticles.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 3;12(8):1583. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081583. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203425 Free PMC article.
-
Ag/Ag3PO4 Nanoparticle-Decorated Hydroxyapatite Functionalized Calcium Carbonate: Ultrasound-Assisted Sustainable Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Activity.Materials (Basel). 2023 Feb 4;16(4):1338. doi: 10.3390/ma16041338. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836970 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Silver Nanoparticles in Parasite Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 21;15(7):1783. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071783. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37513969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: a review.Biometals. 2023 Aug;36(4):745-776. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00479-1. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Biometals. 2023. PMID: 36482125 Review.
References
-
- Togashi T, Tsuchida K, Soma S, Nozawa R, Matsui J, Kanaizuka K, Kurihara M. Size-tunable continuous-seed-mediated growth of silver nanoparticles in alkylamine mixture via the stepwise thermal decomposition of silver oxalate. Chem. Mater. 2020;32:9363–9370. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c03303. - DOI
-
- Cascio C, Geiss O, Franchini F, Ojea-Jimenez I, Rossi F, Gilliland D, Calzolai L. Detection, quantification and derivation of number size distribution of silver nanoparticles in antimicrobial consumer products. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015;30:1255–1265. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00410H. - DOI
-
- Cobley CM, Skrabalak SE, Campbell DJ, Xia Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles for plasmonic and sensing applications. Plasmon. 2009;4:171–179. doi: 10.1007/s11468-009-9088-0. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

