3,6'-disinapoyl sucrose attenuates Aβ1-42 - induced neurotoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans by enhancing antioxidation and regulating autophagy
- PMID: 35044105
- PMCID: PMC8831957
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17153
3,6'-disinapoyl sucrose attenuates Aβ1-42 - induced neurotoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans by enhancing antioxidation and regulating autophagy
Abstract
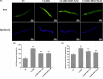
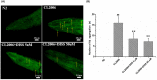
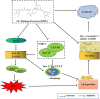
The aggregation of β-amyloid (Aβ) has the neurotoxicity, which is thought to play critical role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Inhibiting Aβ deposition and neurotoxicity has been considered as an important strategy for AD treatment. 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose (DISS), one of the oligosaccharide esters derived from traditional Chinese medicine Polygalae Radix, possesses antioxidative activity, neuroprotective effect and anti-depressive activity. This study was to explore whether DISS could attenuate the pathological changes of Aβ1-42 transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). The results showed that DISS (5 and 50 μM) treatment significantly prolonged the life span, increased the number of egg-laying, reduced paralysis rate, decreased the levels of lipofuscin and ROS and attenuated Aβ deposition in Aβ1-42 transgenic C. elegans. Gene analysis showed that DISS could up-regulate the mRNA expression of sod-3, gst-4, daf-16, bec-1 and lgg-1, while down-regulate the mRNA expression of daf-2 and daf-15 in Aβ1-42 transgenic C. elegans. These results suggested that DISS has the protective effect against Aβ1-42 -induced pathological damages and prolongs the life span of C. elegans, which may be related to the reduction of Aβ deposition and neurotoxicity by regulating expression of genes related to antioxidation and autophagy.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; 3,6'-disinapoyl sucrose; Alzheimer's disease; autophagy; oxidative stress; β-amyloid.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Monascin from Monascus-Fermented Products Reduces Oxidative Stress and Amyloid-β Toxicity via DAF-16/FOXO in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Sep 28;64(38):7114-20. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02779. Epub 2016 Sep 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27554775
-
Lycium ruthenicum Murray exosome-like nanovesicles alleviated Alzheimer's disease-like symptoms induced by Aβ protein in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans through the DAF-16 pathway.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Apr;304(Pt 1):140758. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140758. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39922347
-
rBTI reduced β-amyloid-induced toxicity by promoting autophagy-lysosomal degradation via DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Exp Gerontol. 2017 Mar;89:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.01.018. Epub 2017 Jan 22. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 28119052
-
Alzheimer's disease drug discovery: in vivo screening using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for β-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2013 Spring;10(1):e115-e119. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2012.02.002. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2013. PMID: 24050239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans as a model host to study effects of lactic acid bacteria and functional food factors.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2025 Feb 20;89(3):324-331. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbae172. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39577859 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of the botany, metabolites, pharmacology, toxicity, industrial applications, and processing of Polygalae Radix: the "key medicine for nourishing life".Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 18;15:1450733. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1450733. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39359244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Jiawei Kongsheng Zhenzhong Pill: marker compounds, absorption into the serum (rat), and Q-markers identified by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 5;15:1328632. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1328632. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38375037 Free PMC article.
-
Exendin-4 alleviates β-Amyloid peptide toxicity via DAF-16 in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Aug 5;14:955113. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.955113. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35992601 Free PMC article.
-
Versatility of Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model Organism for Evaluating Foodborne Neurotoxins and Food Bioactive Compounds in Nutritional Neuroscience.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;62(6):7205-7229. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04705-y. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39863742 Review.
-
Label-Free Proteomic Profiling of the dvls2 (CL2006) Caenorhabditis elegans Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Model Reveals Conserved Molecular Signatures Shared With the Human AD Brain.J Neurochem. 2025 Jul;169(7):e70152. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70152. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40653809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atri A. The Alzheimer's disease clinical spectrum: diagnosis and management. Med Clin North Am. 2019;2:263‐293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

