Loss of IRF2BPL impairs neuronal maintenance through excess Wnt signaling
- PMID: 35044823
- PMCID: PMC8769555
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl5613
Loss of IRF2BPL impairs neuronal maintenance through excess Wnt signaling
Abstract
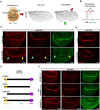
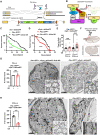
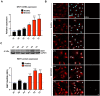
De novo truncations in Interferon Regulatory Factor 2 Binding Protein Like (IRF2BPL) lead to severe childhood-onset neurodegenerative disorders. To determine how loss of IRF2BPL causes neural dysfunction, we examined its function in Drosophila and zebrafish. Overexpression of either IRF2BPL or Pits, the Drosophila ortholog, represses Wnt transcription in flies. In contrast, neuronal depletion of Pits leads to increased wingless (wg) levels in the brain and is associated with axonal loss, whereas inhibition of Wg signaling is neuroprotective. Moreover, increased neuronal expression of wg in flies is sufficient to cause age-dependent axonal loss, similar to reduction of Pits. Loss of irf2bpl in zebrafish also causes neurological defects with an associated increase in wnt1 transcription and downstream signaling. WNT1 is also increased in patient-derived astrocytes, and pharmacological inhibition of Wnt suppresses the neurological phenotypes. Last, IRF2BPL and the Wnt antagonist, CKIα, physically and genetically interact, showing that IRF2BPL and CkIα antagonize Wnt transcription and signaling.
Figures




References
-
- Marcogliese P. C., Shashi V., Spillmann R. C., Stong N., Rosenfeld J. A., Koenig M. K., Martínez-Agosto J. A., Herzog M., Chen A. H., Dickson P. I., Lin H. J., Vera M. U., Salamon N., Graham J. M. Jr., Ortiz D., Infante E., Steyaert W., Dermaut B., Poppe B., Chung H.-L., Zuo Z., Lee P.-T., Kanca O., Xia F., Yang Y., Smith E. C., Jasien J., Kansagra S., Spiridigliozzi G., El-Dairi M., Lark R., Riley K., Koeberl D. D., Golden-Grant K.; Program for Undiagnosed Diseases (UD-Pr OZA); Undiagnosed Diseases Network, Yamamoto S., Wangler M. F., Mirzaa G., Hemelsoet D., Lee B., Nelson S. F., Goldstein D. B., Bellen H. J., Pena L. D. M., IRF2BPL is associated with neurological phenotypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 103, 245–260 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mau-Them F. T., Guibaud L., Duplomb L., Keren B., Lindstrom K., Marey I., Mochel F., van den Boogaard M. J., Oegema R., Nava C., Masurel A., Jouan T., Jansen F. E., Au M., Chen A. H., Cho M., Duffourd Y., Lozier E., Konovalov F., Sharkov A., Korostelev S., Urteaga B., Dickson P., Vera M., Martínez-Agosto J. A., Begemann A., Zweier M., Schmitt-Mechelke T., Rauch A., Philippe C., van Gassen K., Nelson S., Graham J. M. Jr., Friedman J., Faivre L., Lin H. J., Thauvin-Robinet C., Vitobello A., De novo truncating variants in the intronless IRF2BPL are responsible for developmental epileptic encephalopathy. Genet. Med. 21, 1008–1014 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Rampazzo A., Pivotto F., Occhi G., Tiso N., Bortoluzzi S., Rowen L., Hood L., Nava A., Danieli G. A., Characterization of C14orf4, a novel intronless human gene containing a polyglutamine repeat, mapped to the ARVD1 critical region. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 278, 766–774 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Steinhart Z., Angers S., Wnt signaling in development and tissue homeostasis. Development 145, dev146589 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

