Image-guided interventional radiological delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells for pleural malignancies in a phase I/II clinical trial
- PMID: 35045358
- PMCID: PMC9256852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.01.003
Image-guided interventional radiological delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells for pleural malignancies in a phase I/II clinical trial
Abstract
Objectives: We describe techniques and results of image-guided delivery of mesothelin-targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in patients with pleural malignancies in a phase I/II trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02414269).
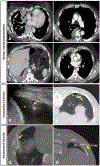
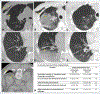
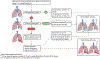
Materials and methods: Patients without a pleural catheter or who lack effusion for insertion of a catheter (31 of 41) were administered intrapleural CAR T cells by interventional radiologists under image guidance by computed tomography or ultrasound. CAR T cells were administered through a needle in an accessible pleural loculation (intracavitary) or following an induced loculated artificial pneumothorax. In patients where intracavitary infusion was not feasible, CAR T cells were injected via percutaneous approach either surrounding and/or in the pleural nodule/thickening (intratumoral). Pre- and post-procedural clinical, laboratory, and imaging findings were assessed.
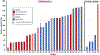
Results: CAR T cells were administered intrapleurally in 31 patients (33 procedures, 2 patients were administered a second dose) with successful delivery of planned dose (10-186 mL); 14/33 (42%) intracavitary and 19/33 (58%) intratumoral. All procedures were completed within 2 h of T-cell thawing. There were no procedure-related adverse events greater than grade 1 (1 in 3 patients had prior ipsilateral pleural fusion procedures). The most common imaging finding was ground glass opacities with interlobular septal thickening and/or consolidation, observed in 12/33 (36%) procedures. There was no difference in the incidence of fever, CRP, IL-6, and peak vector copy number in the peripheral blood between infusion methods.
Conclusion: Image-guided intrapleural delivery of CAR T cells using intracavitary or intratumoral routes is feasible, repeatable and safe across anatomically variable pleural cancers.
Keywords: Adoptive cell therapy; Malignant pleural effusion; Malignant pleural mesothelioma; Pleural metastases; Regional delivery.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, Rives S, Boyer M, Bittencourt H, Bader P, Verneris MR, Stefanski HE, Myers GD, Qayed M, De Moerloose B, Hiramatsu H, Schlis K, Davis KL, Martin PL, Nemecek ER, Yanik GA, Peters C, Baruchel A, Boissel N, Mechinaud F, Balduzzi A, Krueger J, June CH, Levine BL, Wood P, Taran T, Leung M, Mueller KT, Zhang Y, Sen K, Lebwohl D, Pulsipher MA, Grupp SA, Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia, N Engl J Med 378(5) (2018) 439–448. 10.1056/NEJMoa1709866 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Park JH, Riviere I, Gonen M, Wang X, Senechal B, Curran KJ, Sauter C, Wang Y, Santomasso B, Mead E, Roshal M, Maslak P, Davila M, Brentjens RJ, Sadelain M, Long-term follow-up of CD19 CAR therapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia, N Engl J Med 378(5) (2018) 449–459. 10.1056/NEJMoa1709919 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schuster SJ, Svoboda J, Chong EA, Nasta SD, Mato AR, Anak Ö, Brogdon JL, Pruteanu-Malinici I, Bhoj V, Landsburg D, Wasik M, Levine BL, Lacey SF, Melenhorst JJ, Porter DL, June CH, Chimeric antigen receptor T cells in refractory B-cell lymphomas, N Engl J Med 377(26) (2017) 2545–2554. 10.1056/NEJMoa1708566 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adusumilli PS, Cherkassky L, Villena-Vargas J, Colovos C, Servais E, Plotkin J, Jones DR, Sadelain M, Regional delivery of mesothelin-targeted CAR T cell therapy generates potent and long-lasting CD4-dependent tumor immunity, Sci Transl Med 6(261) (2014) 261ra151. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3010162 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

