Clinical efficacy of iodine complex in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients with mild to moderate symptoms: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 35045888
- PMCID: PMC8767036
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-021-05848-8
Clinical efficacy of iodine complex in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients with mild to moderate symptoms: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by the novel coronavirus-infected millions globally. Despite a wide range of advised options for the treatment of COVID-19, a single strategy to tackle this pandemic remains elusive, thus far. That is why we are conducting a clinical trial to find out the efficacy of iodine complex to clear a viral load of severe respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) along with a reduction in time taken to alleviate symptoms.
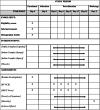
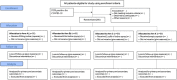
Method: The proposed study is a placebo-controlled, add-on, randomized trial using parallel group designs. This is a closed-label and adaptive with sample size reassessment, multi-centered design with a 1:1:1:1 allocation ratio and superiority framework. It will be conducted in Shaikh Zayed Post-Graduate Medical Complex, Ali Clinic, and Doctors Lounge, Lahore, Pakistan. This study will have three arms of mild to moderately symptomatic COVID-19 patients (50 patients in each) which will receive ionic-iodine polymer complex with 200 mg of elemental iodine: interventional arm A will have encapsulated, arm B will receive suspension syrup form, arm C will get throat spray, while arm X will be standard care with placebo. Data will be collected on self-constructed, close-ended questionnaires after obtaining written consent. Data will be analyzed using SAS version 9.4. COVID-19 patients will be monitored by RT-PCR and HRCT (high-resolution computed tomography) chest. In addition to these, the duration of the symptomatic phase and mortality benefits will be analyzed in both groups.
Discussion: The study is designed to measure the superior efficacy of the iodine complex as an add-on in treating COVID-19-positive patients with mild to moderate symptoms. This combination is hypothesized to improve various parameters like rapid viral load reduction, clinical and radiological improvement, lower mortality, and reduction in hospitalization. The trial will aid in devising a better strategy to cope with COVID-19 in a relatively inexpensive and accessible way. The implications are global, and this could prove itself to be the most manageable intervention against COVID-19 especially for patients from limited-resource countries with deprived socioeconomic status.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04473261 . Registered on July 16, 2020.
Keywords: COVID-19; Iodine; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that they have no competing interests, and according to the standards of scientific integrity, the publication of both positive and negative study results will be ensured. All the study data (if reasonable) will be made accessible guided by the FAIR principles along with the perspective of relevant laws and privacy regulations. Authorship eligibility follows conventional academic standards. No professional writers had been involved in this.
Figures
References
-
- (WHO) WhO . WHO situation report on coronavirus disease (COVID-19) 2020.
-
- Organization WH . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): situation report, 72. 2020. Household Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Prevalence.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous