Injectable amnion hydrogel-mediated delivery of adipose-derived stem cells for osteoarthritis treatment
- PMID: 35046053
- PMCID: PMC8794776
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2120968119
Injectable amnion hydrogel-mediated delivery of adipose-derived stem cells for osteoarthritis treatment
Abstract
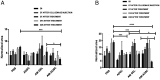
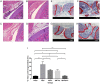
Current treatment strategies for osteoarthritis (OA) predominantly address symptoms with limited disease-modifying potential. There is a growing interest in the use of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) for OA treatment and developing biomimetic injectable hydrogels as cell delivery systems. Biomimetic injectable hydrogels can simulate the native tissue microenvironment by providing appropriate biological and chemical cues for tissue regeneration. A biomimetic injectable hydrogel using amnion membrane (AM) was developed which can self-assemble in situ and retain the stem cells at the target site. In the present study, we evaluated the efficacy of intraarticular injections of AM hydrogels with and without ADSCs in reducing inflammation and cartilage degeneration in a collagenase-induced OA rat model. A week after the induction of OA, rats were treated with control (phosphate-buffered saline), ADSCs, AM gel, and AM-ADSCs. Inflammation and cartilage regeneration was evaluated by joint swelling, analysis of serum by cytokine profiling and Raman spectroscopy, gross appearance, and histology. Both AM and ADSC possess antiinflammatory and chondroprotective properties to target the sites of inflammation in an osteoarthritic joint, thereby reducing the inflammation-mediated damage to the articular cartilage. The present study demonstrated the potential of AM hydrogel to foster cartilage tissue regeneration, a comparable regenerative effect of AM hydrogel and ADSCs, and the synergistic antiinflammatory and chondroprotective effects of AM and ADSC to regenerate cartilage tissue in a rat OA model.
Keywords: adipose-derived stem cells; injectable amnion hydrogel; osteoarthritis; self-targeting property; stem cell therapy.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: A patent titled “Injectable Amnion Hydrogel as a Cell Delivery System” has been filed and published on behalf of the inventors, C.T.L., L.S.N., and M.B. L.S.N. has competing financial interest with Soft Tissue Regeneration/Biorez. C.T.L. has the following competing financial interests: Mimedx (a company that makes amnion-based biologics), Alkermes Company, Biobind, Soft Tissue Regeneration/Biorez, and Healing Orthopaedic Technologies-Bone.
Figures





References
-
- Glyn-Jones S., et al. , Osteoarthritis. Lancet 386, 376–387 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Kotlarz H., Gunnarsson C. L., Fang H., Rizzo J. A., Insurer and out-of-pocket costs of osteoarthritis in the US: Evidence from national survey data. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 3546–3553 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J., Abramson S. B., Osteoarthritis, an inflammatory disease: Potential implication for the selection of new therapeutic targets. Arthritis Rheum. 44, 1237–1247 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

